Agricultural engineering, with its origins in 6000 BC Mesopotamia, revolutionized early human civilizations.
Early innovations like irrigation systems and the seed plow greatly increased agricultural efficiency.
The 20th century witnessed a transformative moment with the advent of the tractor, significantly changing farming methods.
Today, this field blends traditional techniques with advanced technologies like GPS and drones, underscoring the continuous evolution of agricultural practices and their significance in our daily lives.
This article delves into fun facts about agricultural engineering, highlighting its profound impact through the ages.
1. Ancient Roots of Agricultural Engineering
Agricultural engineering’s earliest known roots trace back to around 6000 BC in Mesopotamia.
It was here that one of humanity’s first known irrigation systems was developed, a groundbreaking advancement for its time.
This innovation allowed the Mesopotamians to control river water flow, crucial for crop cultivation in an otherwise arid landscape.
The invention of the seed plow, another significant achievement, greatly improved sowing methods, directly contributing to increased agricultural productivity and the rise of early civilizations.
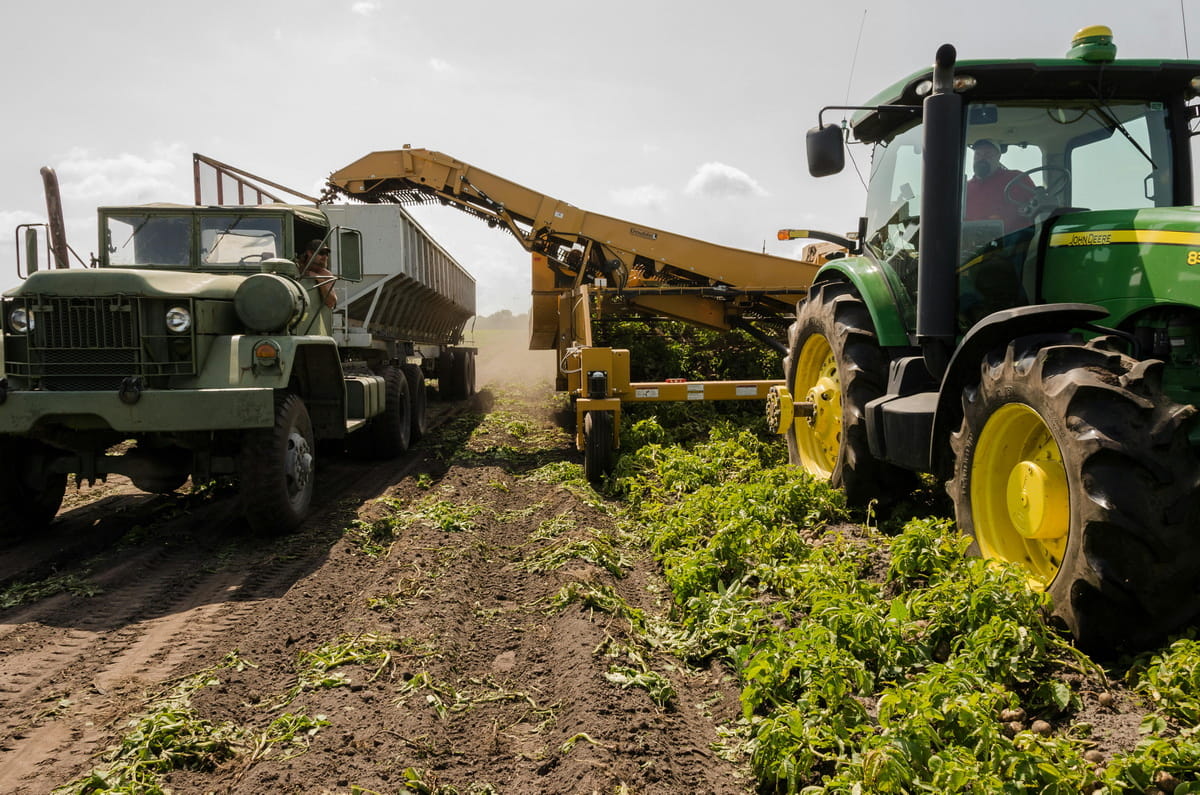
2. Tractors: Revolutionizing Modern Farming
The modern tractor, emerging in the early 1900s, marked a pivotal shift from animal to mechanical labor in agriculture.
Its introduction dramatically increased farming efficiency, changing the agricultural landscape forever.
By the 1930s, the addition of rubber tires to tractors represented another major leap, significantly enhancing their operational efficiency and reducing soil compaction.
This evolution of the tractor not only transformed farming practices but also catalyzed a broader mechanization in agricultural sectors worldwide.
3. Innovations in Agricultural Irrigation
Drip irrigation, introduced in Israel in 1965, marked a watershed moment in agricultural water management.
This method revolutionized the efficiency of water use in farming, allowing precise delivery of water directly to plant roots.
Subsequent innovations, like sensor-based systems, have further optimized irrigation practices, enabling cultivation in arid regions and enhancing global food security.
4. GPS and Drones in Precision Agriculture
The incorporation of GPS technology into agriculture in the 1990s revolutionized the precision and efficiency of farming practices.
It enabled farmers to accurately map fields, apply resources variably, and optimize crop management strategies.
The advent of drone technology in the 2010s further enhanced agricultural efficiency, providing high-resolution imagery for improved crop monitoring and management.
These technological advancements have not only boosted productivity but also contributed to more environmentally sustainable farming practices.
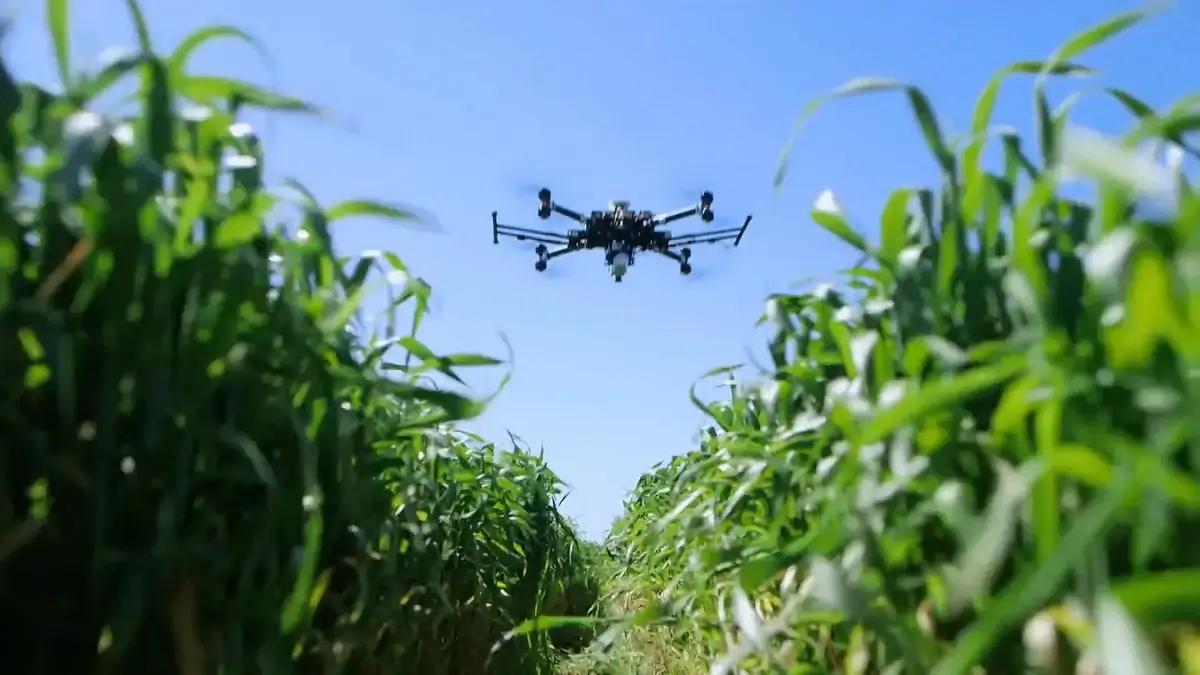

Image: Britannica
5. Eco-Friendly Farming and Agri Engineering
The rise of eco-friendly farming in the late 20th century was significantly bolstered by advances in agricultural engineering.
Key developments included the refinement of sustainable soil management techniques and water conservation methods, reducing the environmental footprint of farming.
Technologies like crop rotation and natural pest control, integrated with engineering solutions, have led to more sustainable crop yields.
This shift towards eco-friendly practices not only preserves environmental health but also ensures long-term agricultural productivity.
6. The Green Revolution’s Engineering Impact
The Green Revolution, spanning the 1940s to the late 1960s, was marked by significant agricultural engineering breakthroughs.
High-yield crop varieties were developed, and synthetic fertilizers and pesticides were introduced, vastly increasing global food production.
Irrigation systems were modernized, and mechanization was enhanced, further boosting crop yields.
This period significantly reduced worldwide hunger, although it also raised concerns about environmental sustainability.

Image: Britannica
7. Breakthroughs in Soil Science and Farming
Advancements in soil science, a critical component of agricultural engineering, have transformed farming practices.
The development of soil testing techniques in the mid-20th century allowed for more precise nutrient management, optimizing crop growth.
Understanding soil microbiology and its impact on plant health has led to more effective soil conservation strategies.
These breakthroughs have significantly improved soil fertility management, directly contributing to increased agricultural productivity.
8. Robotic Technology in Modern Agriculture
The integration of robotics into agriculture, gaining momentum in the 21st century, has revolutionized farming operations.
Autonomous tractors, drones, and robotic harvesters enhance efficiency, reduce labor needs, and increase precision in farming tasks.
Robotics in greenhouse management and livestock farming has also improved production quality and animal welfare.
This technological shift is defining the future of agriculture, combining efficiency with sustainability.
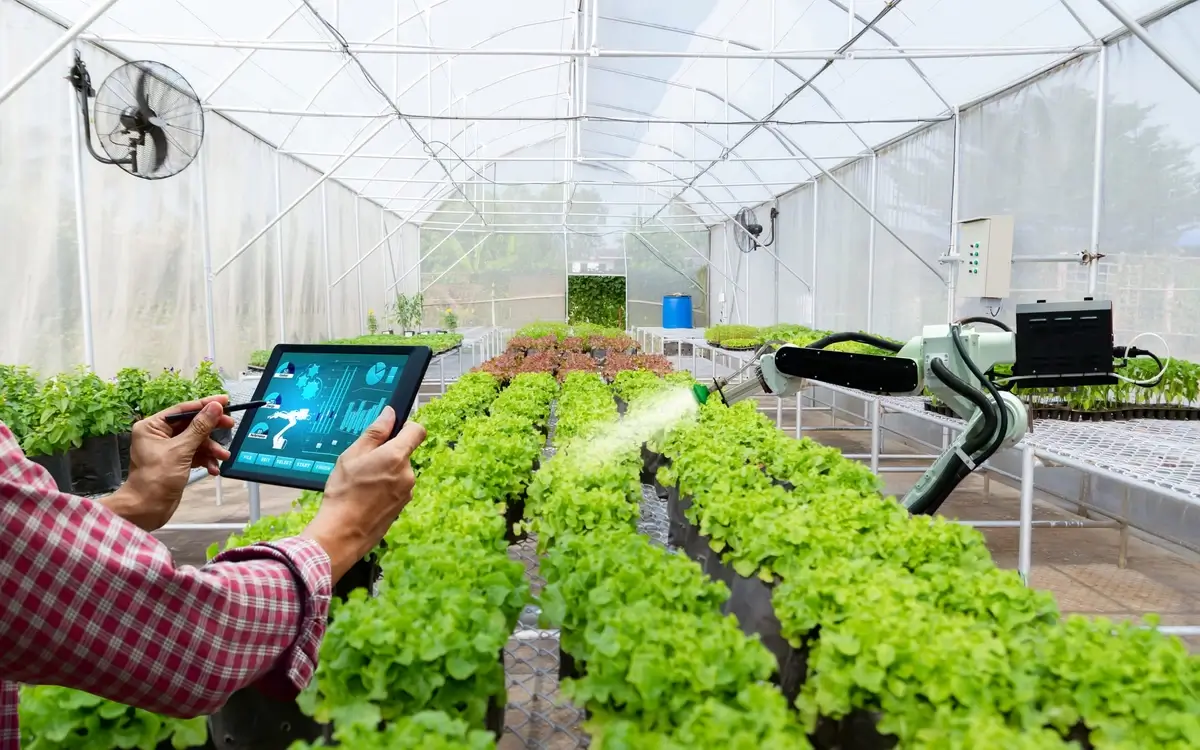

Image: hdi.global
9. Bioenergy: Agriculture’s Renewable Source
Bioenergy, derived from agricultural products and by-products, has emerged as a key renewable energy source.
Biomass from crop residues, animal manure, and dedicated energy crops are converted into biofuels, contributing to sustainable energy solutions.
The development of bioenergy not only provides an alternative to fossil fuels but also adds value to agricultural waste.
This sector’s growth reflects the increasing role of agricultural engineering in addressing global energy challenges.
10. Adapting Farming to Climate Change
Agricultural engineering has been pivotal in adapting farming practices to the challenges of climate change.
Developments in drought-resistant crop varieties and efficient water management systems have become crucial.
Techniques like no-till farming reduce soil erosion and carbon emissions, helping mitigate climate change effects.
These adaptations are essential for maintaining crop yields and food security in the face of changing environmental conditions.
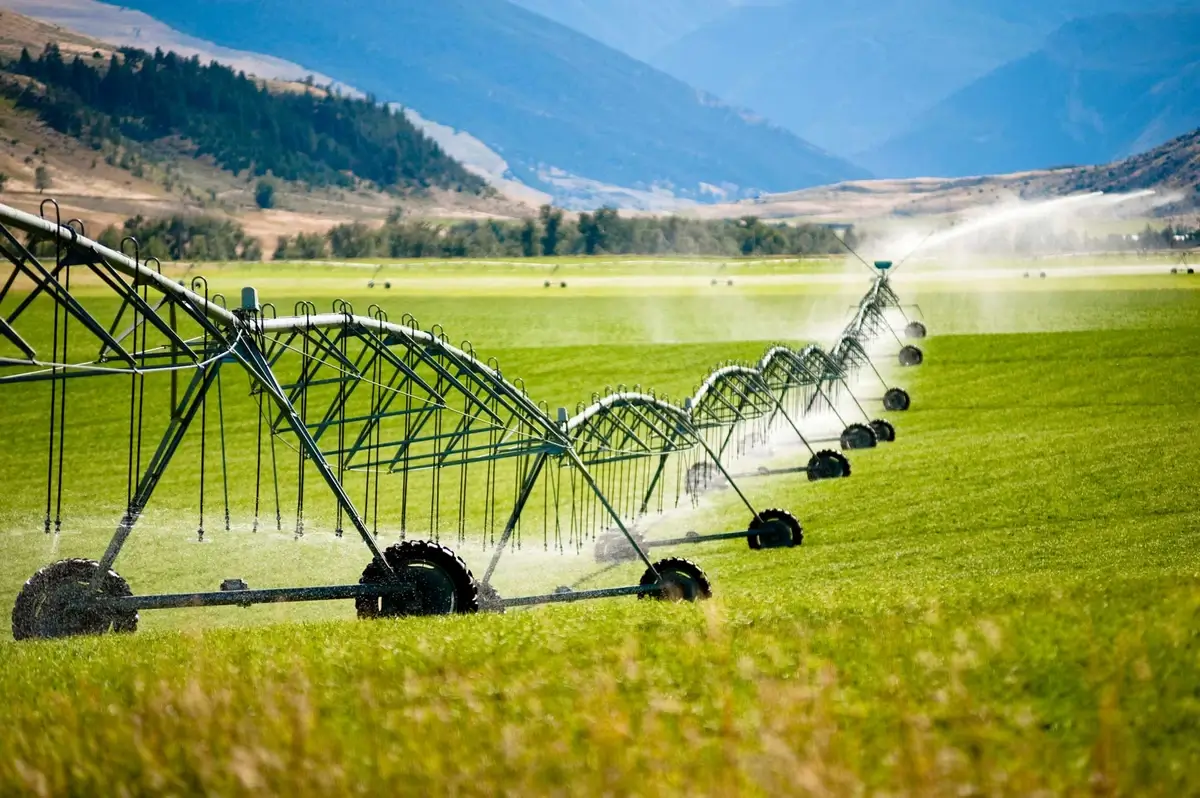

Image: watercalculator.org
11. Hydroponics: Soil-less Farming Innovations
Hydroponics, the cultivation of plants in nutrient-rich water without soil, has revolutionized agriculture.
Developed in the 1930s, this technique allows for year-round cultivation, independent of soil quality and weather conditions.
Hydroponics systems, often combined with controlled environment agriculture, result in higher yields and faster growth rates.
This soil-less farming method is particularly significant for urban and space-constrained environments.
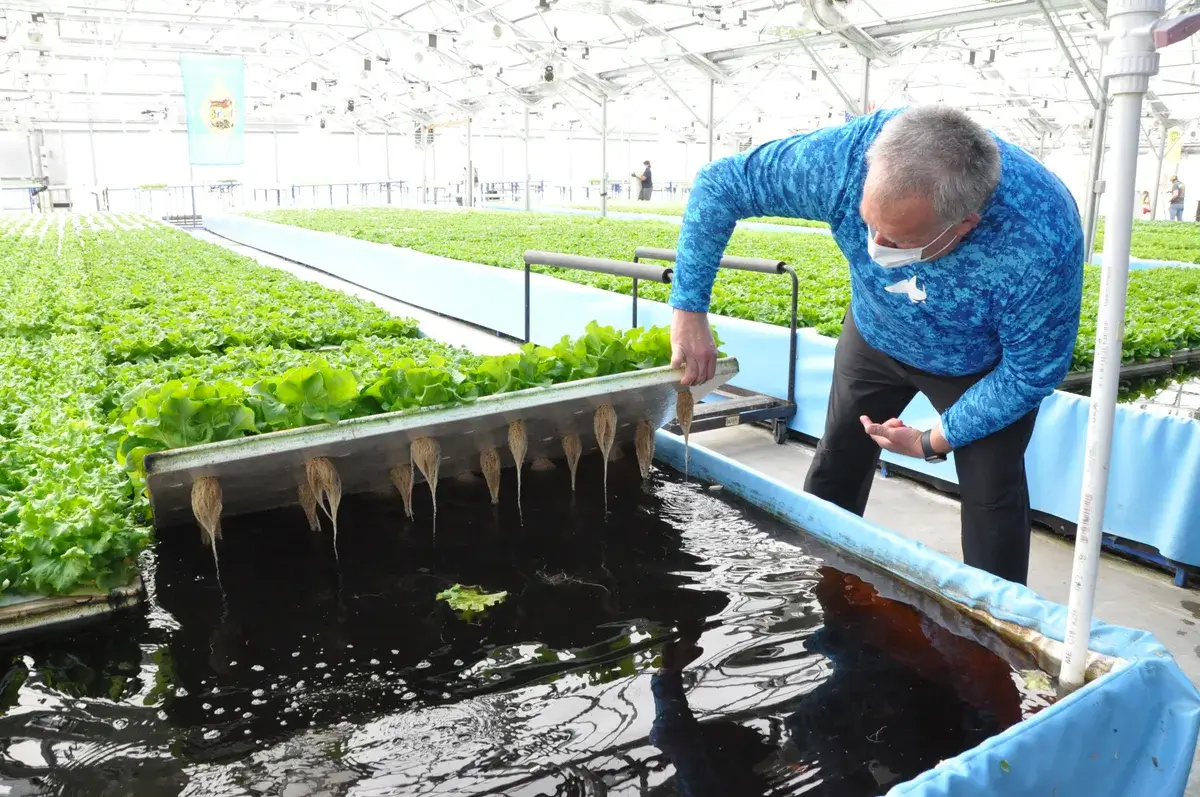

Image: delawareonline.com
12. Genetic Engineering in Crop Production
Genetic engineering in crops, a major breakthrough in the late 20th century, has profoundly impacted agriculture.
It involves altering the DNA of crops to enhance traits like yield, nutritional value, and pest resistance.
Genetically modified (GM) crops have significantly increased global food production but also sparked debates about safety and biodiversity.
This technology continues to evolve, offering potential solutions to food security challenges.
13. Big Data’s Role in Agriculture Today
Big data has become a transformative force in modern agriculture, driving efficiency and sustainability.
Data analytics enable farmers to make informed decisions based on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health.
Technologies like satellite imagery and machine learning offer insights for optimizing resource use and crop yields.
Big data’s integration into agriculture signifies a shift towards more informed and precise farming practices.
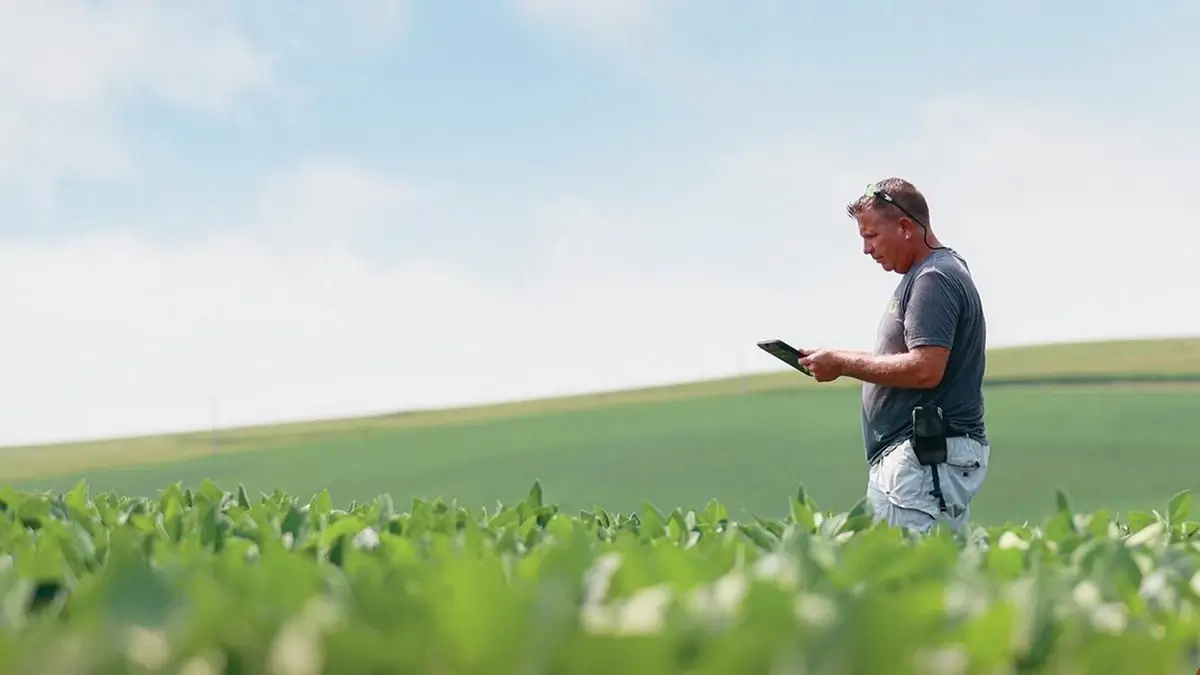

Image: wsj.com
14. Agricultural Engineering and Food Security
Agricultural engineering plays a crucial role in global food security, particularly as the world’s population continues to grow.
Innovations in crop production, irrigation, and soil management contribute significantly to feeding the global population.
Engineering solutions also address challenges like food storage and transportation, reducing post-harvest losses.
This field’s advancements are key to sustaining food availability worldwide.
15. Urban Agriculture: Bringing Farms to the City
Urban agriculture, a growing trend in agricultural engineering, adapts farming practices for city environments.
Innovations like rooftop gardens, vertical farming, and community gardens are transforming urban spaces into productive food sources.
These methods utilize limited space efficiently and reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting food to urban areas.
Urban agriculture not only contributes to local food security but also fosters community engagement and environmental awareness.
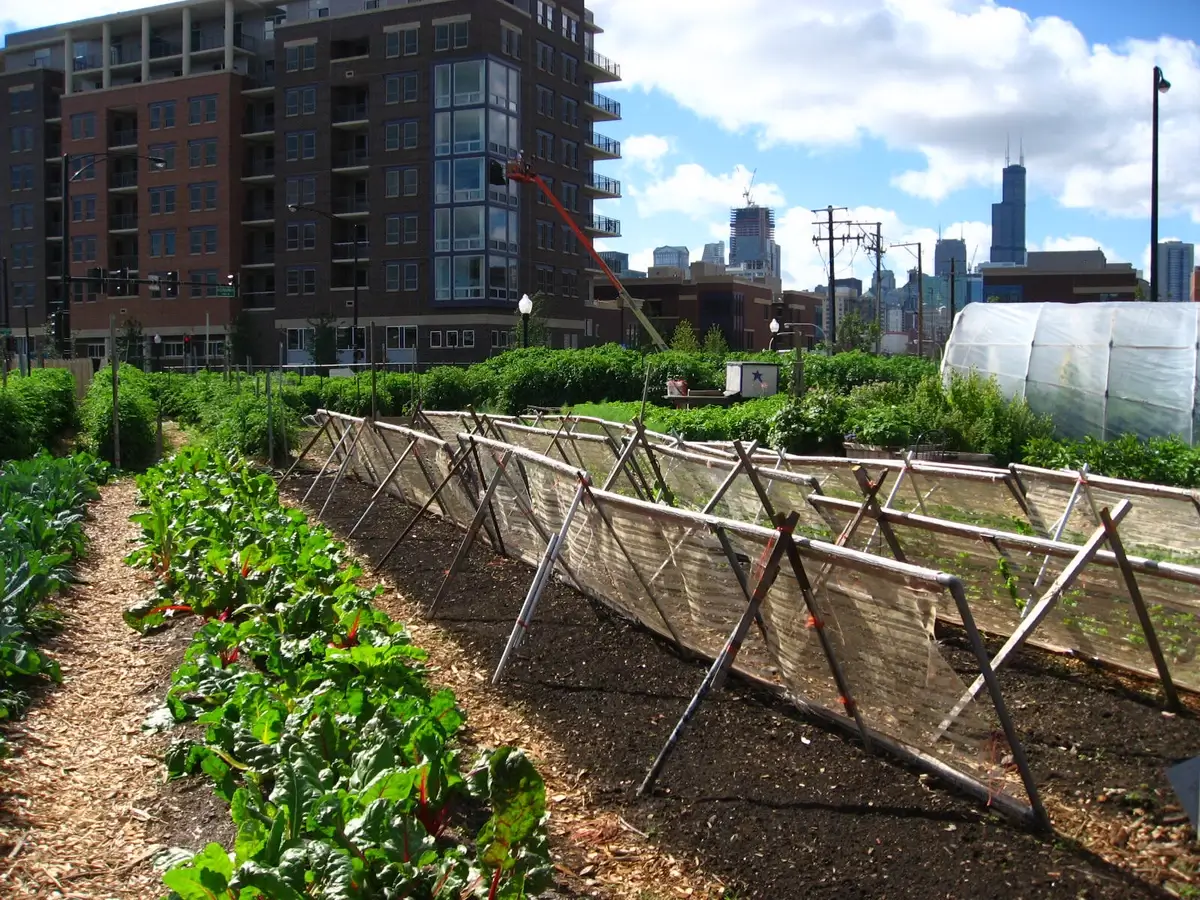

Image: Wikimedia Commons
FAQ
Who is the most famous agricultural engineer?
John Deere, best known for inventing the steel plow in 1837, is often regarded as one of the most influential figures in agricultural engineering. His invention revolutionized farming by significantly improving efficiency and soil management, laying the groundwork for modern agricultural machinery.
What did agricultural engineers invent?
Agricultural engineers have been pivotal in developing various technologies, including advanced irrigation systems, farm machinery like tractors and combines, and soil conservation techniques. They have also contributed to innovations in crop storage and processing, as well as in renewable energy sources related to agriculture, such as biofuels.
What are the benefits of agricultural engineering?
Agricultural engineering offers numerous benefits, including increased crop yields and farming efficiency, improved water and soil management, and the development of sustainable farming practices. It also plays a crucial role in addressing global challenges like food security and the environmental impacts of agriculture.
What do agricultural engineers wear?
Agricultural engineers typically wear clothing suitable for both office and fieldwork. In the field, they might wear protective gear like hard hats, safety glasses, and boots to ensure safety while working with machinery or on-site. For office or lab work, the attire is usually casual or business casual.
Is agricultural engineering a good major?
Agricultural engineering is an excellent major for those interested in solving complex problems related to agriculture and natural resources. It combines principles of engineering with agricultural science, offering diverse career opportunities in areas like farm management, environmental conservation, and agribusiness.
How does agricultural engineering affect society?
Agricultural engineering significantly impacts society by enhancing food production efficiency and sustainability, which is vital for feeding a growing global population. It also contributes to environmental protection through the development of sustainable farming practices and renewable energy sources derived from agricultural by-products.
Which is best agricultural engineering?
The “best” in agricultural engineering can be subjective and depends on specific interests and career goals. Top areas include precision agriculture, which focuses on optimizing field-level management with technology; soil and water conservation; farm machinery design and automation; and agricultural bioengineering. Each area offers unique challenges and opportunities for innovation and impact.