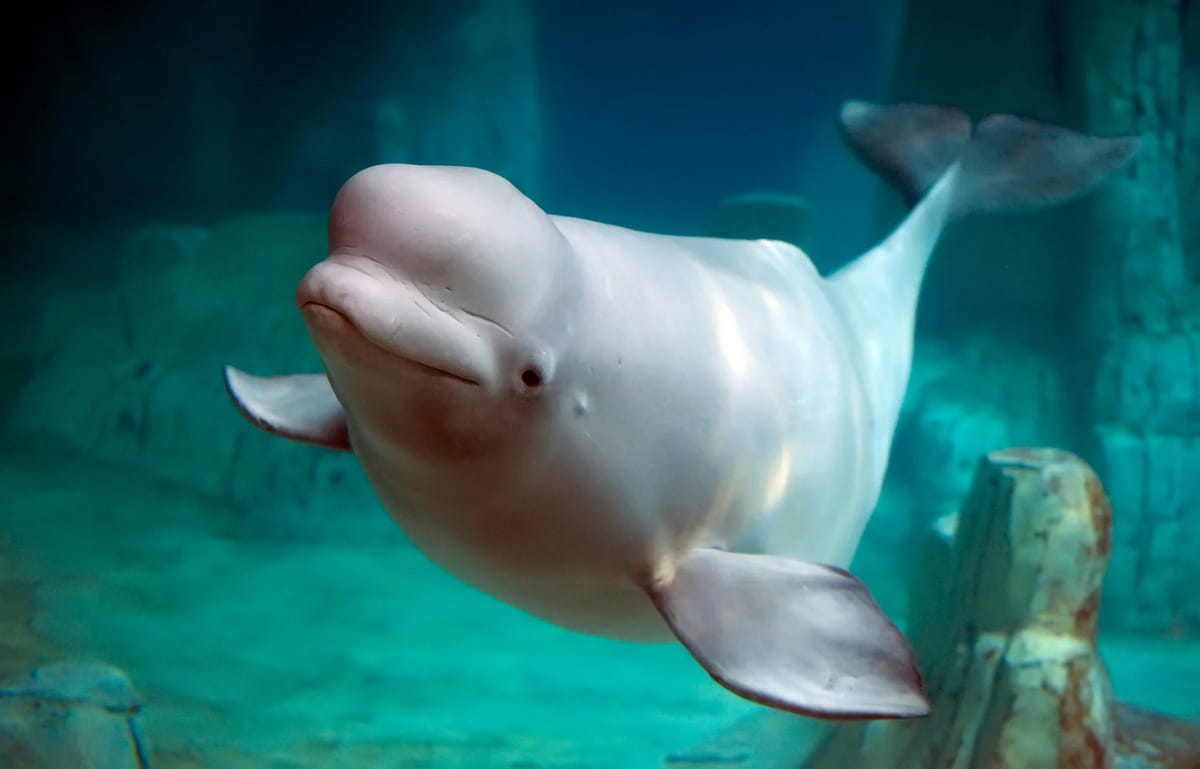
Beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas), often called ‘sea canaries’ due to their wide range of sounds, offer a fascinating study into marine life. These Arctic inhabitants, first described scientifically in 1776, are not just known for their distinctive white color, but also for their unique behaviors and adaptations.
For instance, their ability to survive in freezing Arctic temperatures and their varied diet are subjects of extensive research, providing insights into their ecological significance.
Dive into this article for more fun facts about beluga whales that showcase their remarkable world.
1. Unique Vocalizations: The ‘Canaries of the Sea’
Beluga whales, remarkable for their vocal diversity, use a sophisticated language of clicks, whistles, and clangs. This skill is not just for communication; it’s crucial for their survival in the opaque Arctic waters.
A study by the National Marine Mammal Laboratory indicates that belugas can mimic a variety of other sounds, a rare trait in the animal kingdom. Their ‘songs’ are so diverse that scientists often use them to distinguish individual pods, crucial for tracking their migratory patterns.
2. Beluga Whales: Masters of Facial Expressions
Belugas are one of the few whale species that can make facial expressions, thanks to their unique facial musculature. This rare ability is linked to their echolocation skills. Research from the University of Washington shows that these expressions are vital for their communication, especially in the murky waters they inhabit.
This flexibility in facial muscles is not just an anatomical wonder but also crucial for their social interactions.
3. Adaptation in the Arctic: How Belugas Thrive in Cold
Belugas have a remarkable adaptation to the Arctic’s frigid conditions. Their blubber, up to 6 inches (15 cm) thick, insulates them in temperatures that can plunge below -2°C.
A study by the Arctic University of Norway reveals that belugas can reduce blood flow to their skin to conserve heat, a critical adaptation for survival in icy waters. This physiological trait is key to understanding how marine mammals endure extreme cold.
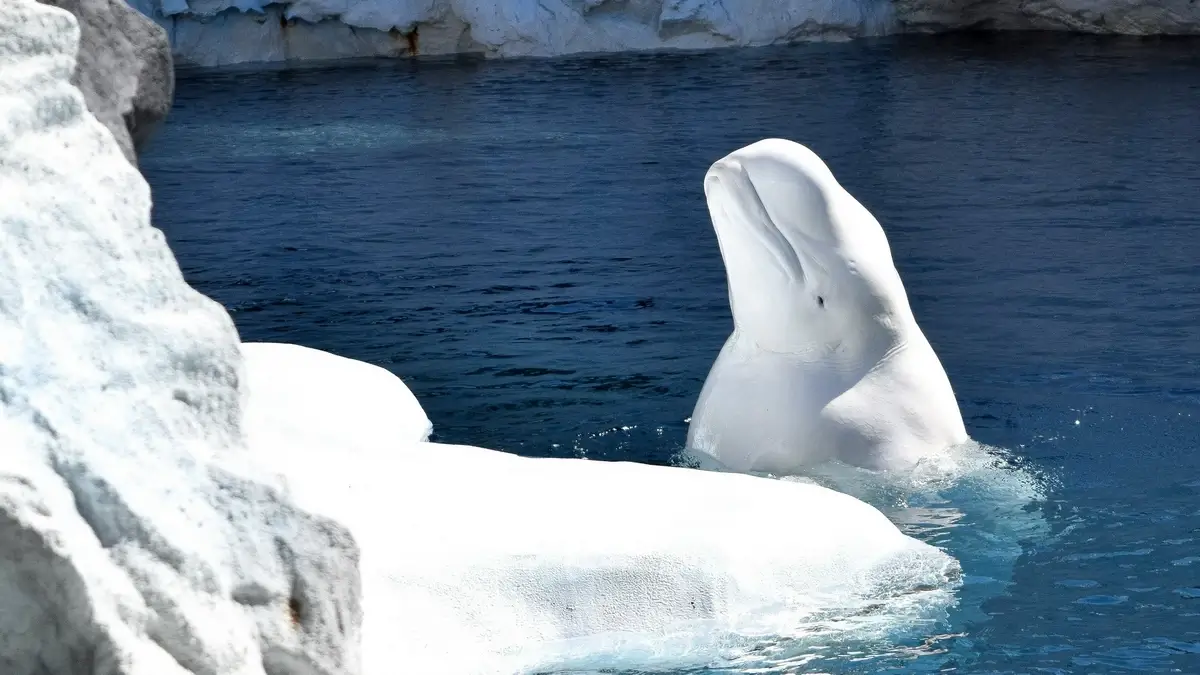

Image: europa.eu
4. Beluga Whales’ Astonishing Diet Variety
Beluga whales have a surprisingly varied diet, crucial for their survival in the Arctic’s challenging ecosystem. They primarily feed on fish like capelin and cod, but also consume crustaceans and cephalopods.
A study by Fisheries and Oceans Canada indicates that their diet varies seasonally and geographically, reflecting the dynamic nature of their habitat. This ability to adapt their diet is essential for their survival in an environment where food availability is often unpredictable.
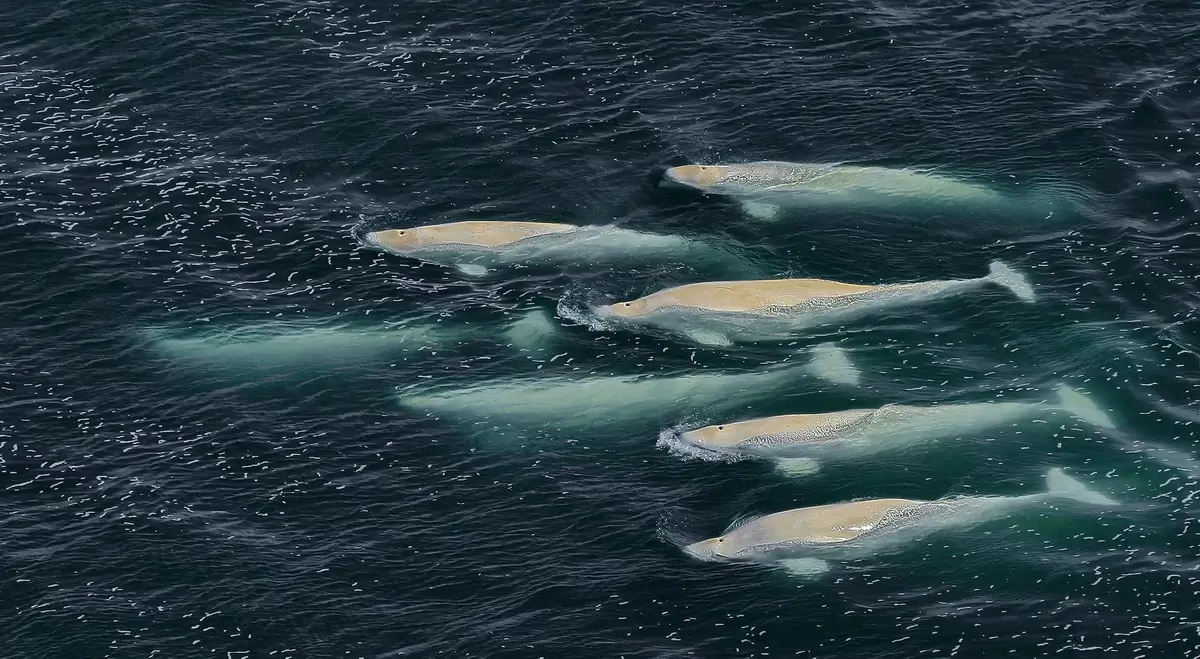

Image: rgo.ru
5. The Migratory Patterns of Beluga Whales
Beluga whales exhibit distinct migratory patterns, largely influenced by the Arctic’s seasonal ice cover. During winter, they move to open waters, avoiding heavy ice, and return to shallow, warmer waters in summer for calving and molting.
According to a study by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game, specific populations, like those in the Beaufort Sea, can travel over 3,700 miles (6,000 kilometers) annually. These migrations are not just impressive in distance but are critical for their survival, ensuring access to food and safe breeding grounds.
6. Beluga Whales: Social and Playful Creatures
Belugas are highly social and exhibit playful behavior, often seen in groups called pods. These pods can range from a few individuals to hundreds.
Research from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) highlights their social structures often include close family ties, with mothers and calves forming strong bonds.
Play is a significant part of their social interaction, involving games and interactions with objects like seaweed, and is believed to be crucial for their cognitive development.
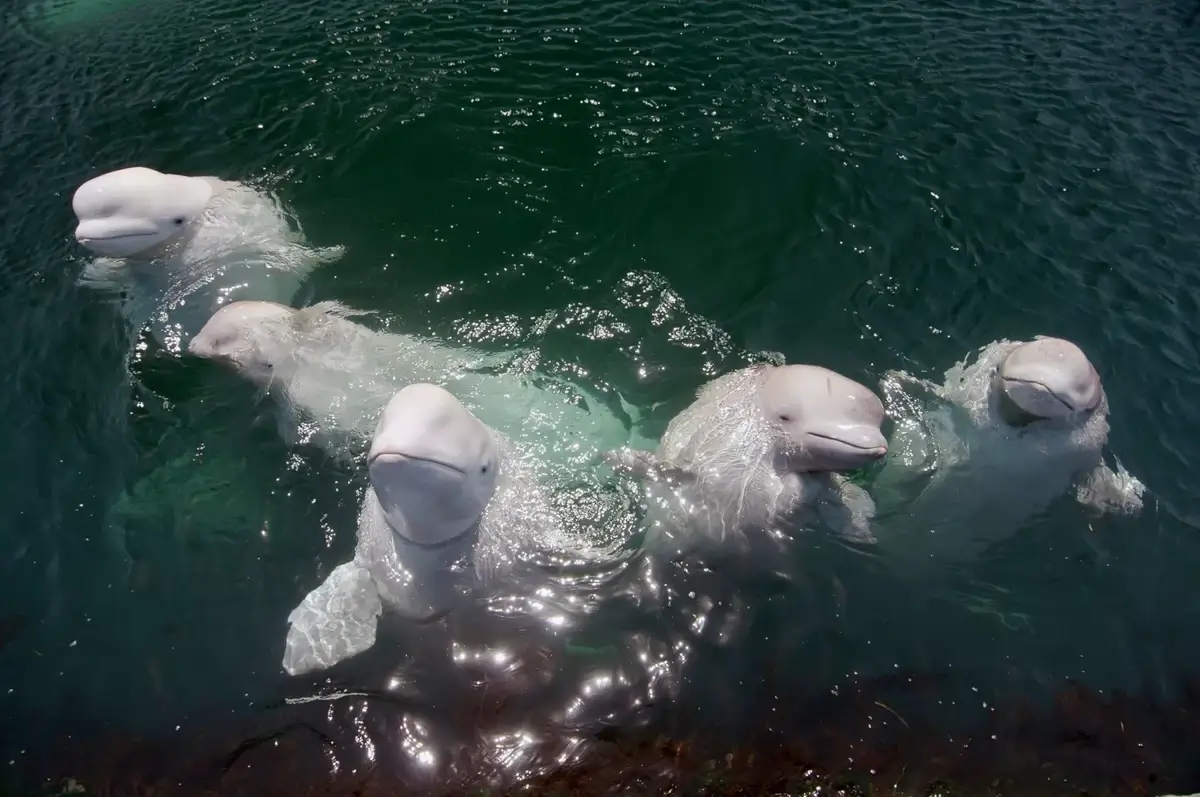

Image: The Mirror
7. The Importance of Beluga Whales in Indigenous Cultures
Beluga whales hold significant cultural and subsistence value in many Indigenous Arctic communities. For centuries, these communities have relied on belugas for food, tools, and materials.
The Smithsonian’s Arctic Studies Center notes that belugas are not only a food source but also integral to the cultural identity and traditional practices of these communities. The respectful approach to hunting and utilization of every part of the whale reflects the deep connection between Indigenous peoples and the Arctic ecosystem.

Image: iFunFact
8. Beluga Whales’ Role in Marine Ecosystems
Beluga whales play a crucial role in their marine ecosystems. As both predator and prey, they help maintain a balanced food web.
A study from the University of Manitoba shows that belugas significantly impact fish populations, which in turn influences the overall health of the marine environment. Moreover, their migratory patterns and feeding habits can provide scientists with valuable indicators of the health and changes in the Arctic ecosystem, making them important species for ecological research.
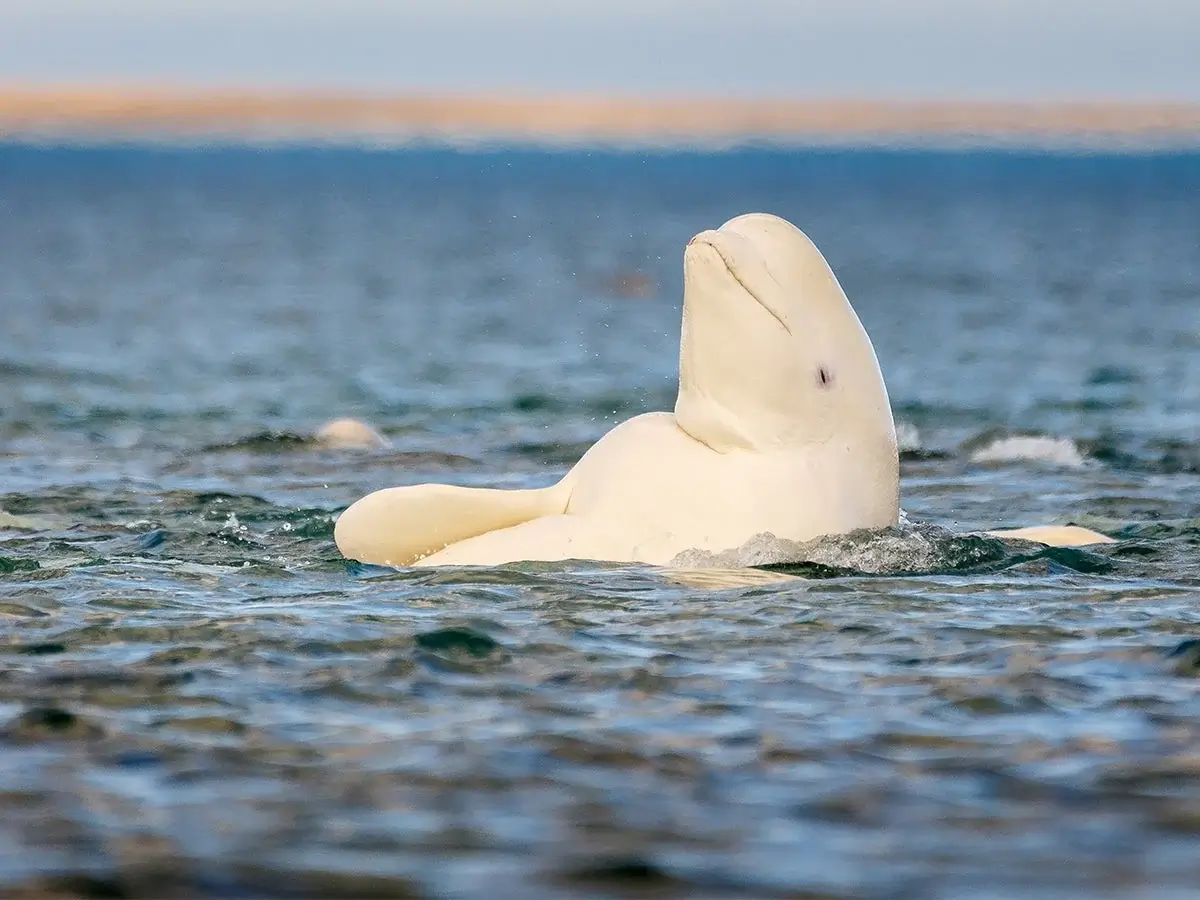

Image: Maria Nila
9. Belugas’ Distinctive Color Change from Birth to Adulthood
One of the most fascinating aspects of beluga whales is their color transformation as they age. Unlike most marine mammals, belugas are born dark gray and gradually lighten as they mature. This transition to white, which occurs around five to seven years of age, is believed to be an adaptation for camouflage in the Arctic ice.
Research from the Marine Mammal Science Association reveals that this color change may also play a role in thermoregulation, as the white color reflects sunlight, helping the whales manage their body temperature.
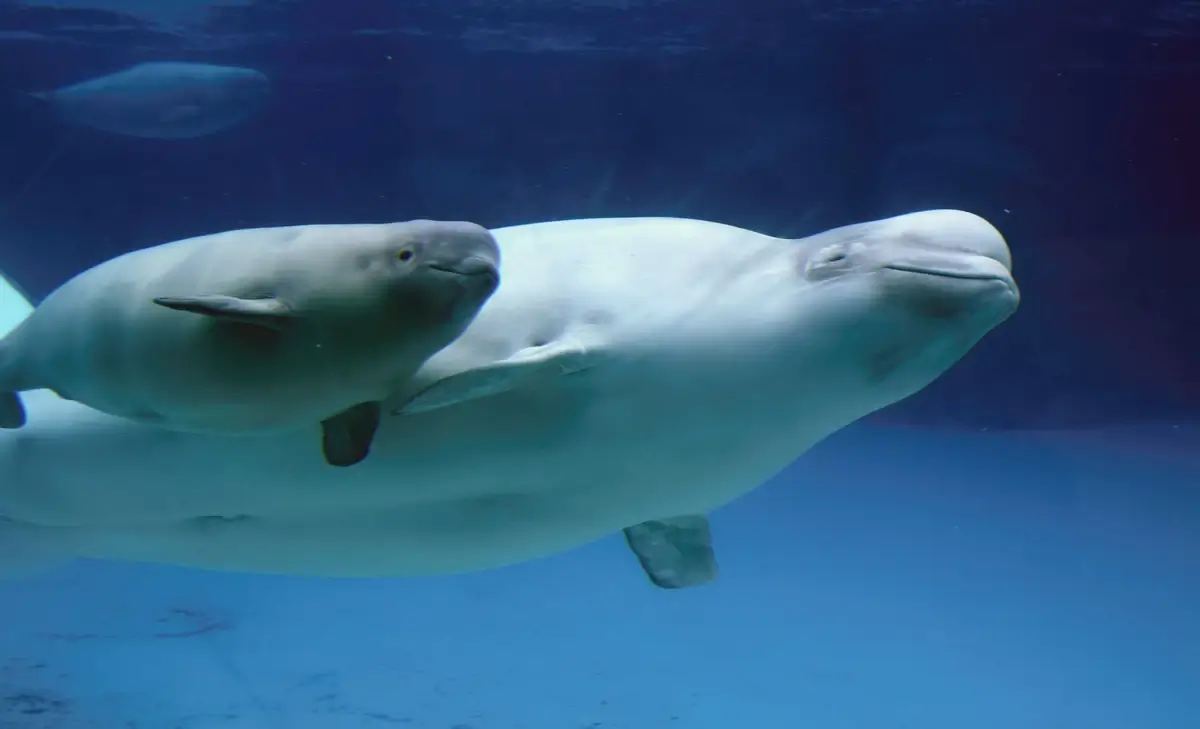

Image: Thermo Fisher Scientific
10. Conservation Efforts for Beluga Whales
Conservation efforts for beluga whales have become increasingly important due to threats like habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Many beluga populations are listed as endangered or near threatened. International efforts, as coordinated by bodies like the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), involve habitat protection, pollution control, and strict regulations on hunting.
Additionally, organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) conduct research and public awareness campaigns to promote beluga conservation. These efforts are crucial for ensuring the survival of these unique marine mammals for future generations.
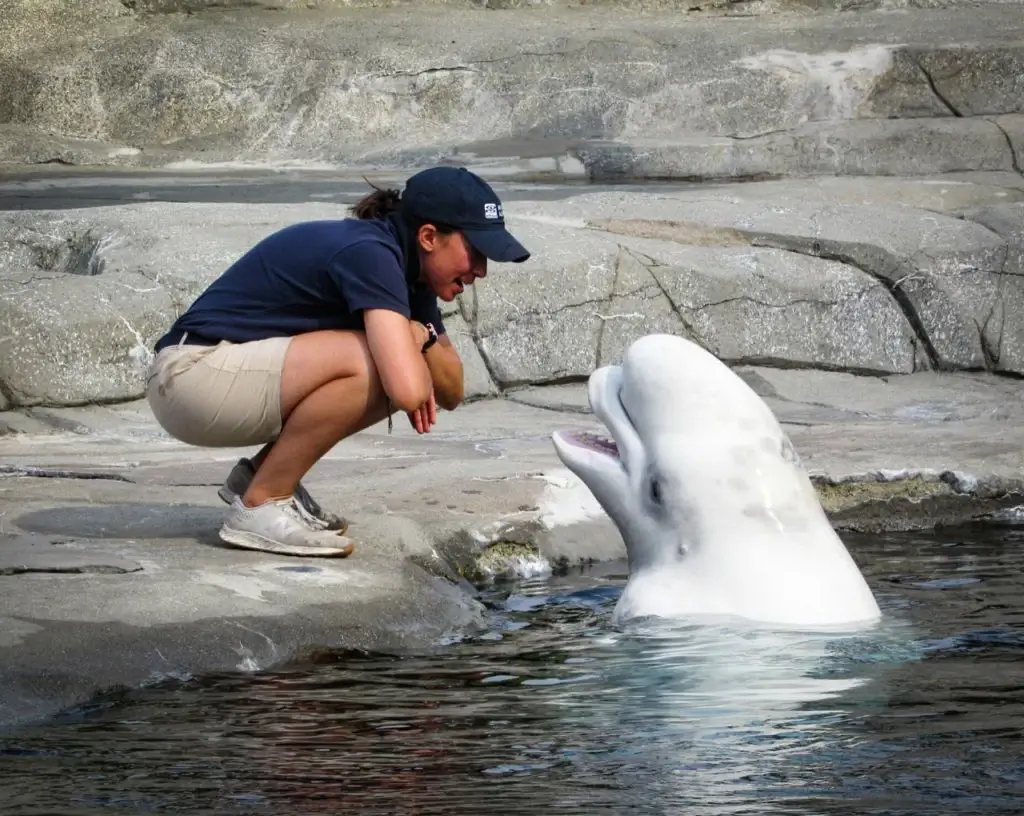

Image: CavalryGroupNewswire.com
FAQ
Why are beluga whales special?
Beluga whales are special due to their distinctive characteristics and behaviors. They are one of the few whale species able to change their facial expressions and are known for their unique vocalizations, earning them the nickname ‘canaries of the sea.’ Their adaptation to Arctic environments, including their ability to navigate and hunt in icy waters, and their social nature also set them apart from other marine mammals.
Why are beluga whales so cute?
Beluga whales are often perceived as cute due to their unique physical features. Their small size compared to other whales, rounded foreheads, and the ability to change facial expressions give them a friendly and approachable appearance. Additionally, their playful behavior and social interactions contribute to this perception of cuteness.
Is beluga whale friendly?
Beluga whales are generally considered friendly, especially in their interactions with humans. They are curious and often approach boats. In captivity, they have been observed to interact playfully with trainers and visitors. However, like all wild animals, their behavior can be unpredictable, and interactions should always be approached with respect and caution.
Are beluga whales deaf?
Beluga whales are not deaf; in fact, they have excellent hearing. Their hearing is highly adapted to their underwater environment. They rely heavily on sound for communication and navigation through echolocation, making their hearing one of their most important senses.
How long do beluga whales live?
Beluga whales typically live for 35 to 50 years, although some individuals have been known to live up to 60 years. Factors such as habitat, diet, and human-induced threats can influence their lifespan.
Are beluga whales colorblind?
It’s believed that beluga whales, like many marine mammals, are likely colorblind or have limited color vision. The underwater environment, where light and color perception differ significantly from on land, makes the ability to perceive a wide range of colors less necessary. Research on marine mammal vision is ongoing, but the current understanding is that their color perception is limited.
How are beluga whales smart?
Beluga whales are considered intelligent based on several behaviors. They show high levels of social complexity, have the ability to learn and adapt to different environments, and use sophisticated vocalizations for communication and echolocation. Their playful behavior and interactions with each other also indicate cognitive abilities. In captivity, they have demonstrated the capacity to learn from trainers and participate in problem-solving tasks.