Fraternal twins, a natural marvel, have captivated interest throughout history.
In 1875, Francis Galton first distinguished between identical and fraternal twins, sparking a scientific quest.
Fraternal twins share about 50% of their DNA, akin to regular siblings but shared a womb.
In 2018, a study revealed that Nigeria has the highest rate of twin births, with a significant number being fraternal.
These twins can be genetically different genders, a phenomenon not possible in identical twins.
This article delves into the fun facts about fraternal twins, blending genetics, history, and culture.
1. Unraveling the Genetics of Fraternal Twins
Fraternal twins result from the fertilization of two separate eggs by two different sperm.
They can have different fathers, a rare occurrence known as heteropaternal superfecundation.
In genetics, they’re termed dizygotic, emphasizing their distinct genetic origins.
Their genetic diversity contributes to varied physical and personality traits, unlike identical twins.
2. Distinguishing Fraternal and Identical Twins
Fraternal twins are as genetically similar as regular siblings, sharing about 50% of their DNA.
Identical twins, however, share nearly 100% of their DNA, originating from a single fertilized egg.
Zygosity testing can confirm if twins are fraternal or identical, crucial for understanding their genetic relationship.
Physical differences in fraternal twins often become evident early, unlike in identical twins.
3. The Fascinating World of Opposite-Sex Fraternal Twins
Opposite-sex fraternal twins are a common occurrence, representing about 40% of all fraternal twins.
Their development from two separate eggs allows for the possibility of one twin being male and the other female.
This phenomenon offers a unique window into gender differences from birth.
Studies show that these twins can exhibit different developmental patterns and behaviors from a young age.
4. Chances of Having Fraternal Twins in Families
Genetics play a significant role in the likelihood of having fraternal twins.
Women with a family history of twins are more likely to conceive twins themselves.
The twin birth rate has risen by over 75% since the 1980s, partly due to fertility treatments.
Older maternal age also increases the chances of fraternal twinning, with the highest likelihood in women aged 35-40.
5. Record-Breaking Facts About Fraternal Twins
In 1996, Molly and Benjamin West set a world record for the longest interval between fraternal twin births at 90 days.
Their birth in Baltimore, Maryland, challenged conventional twin pregnancy timelines.
This case contributes to the understanding of the variability in twin gestation periods.
Medical interest in such rare cases helps advance prenatal and obstetric care.
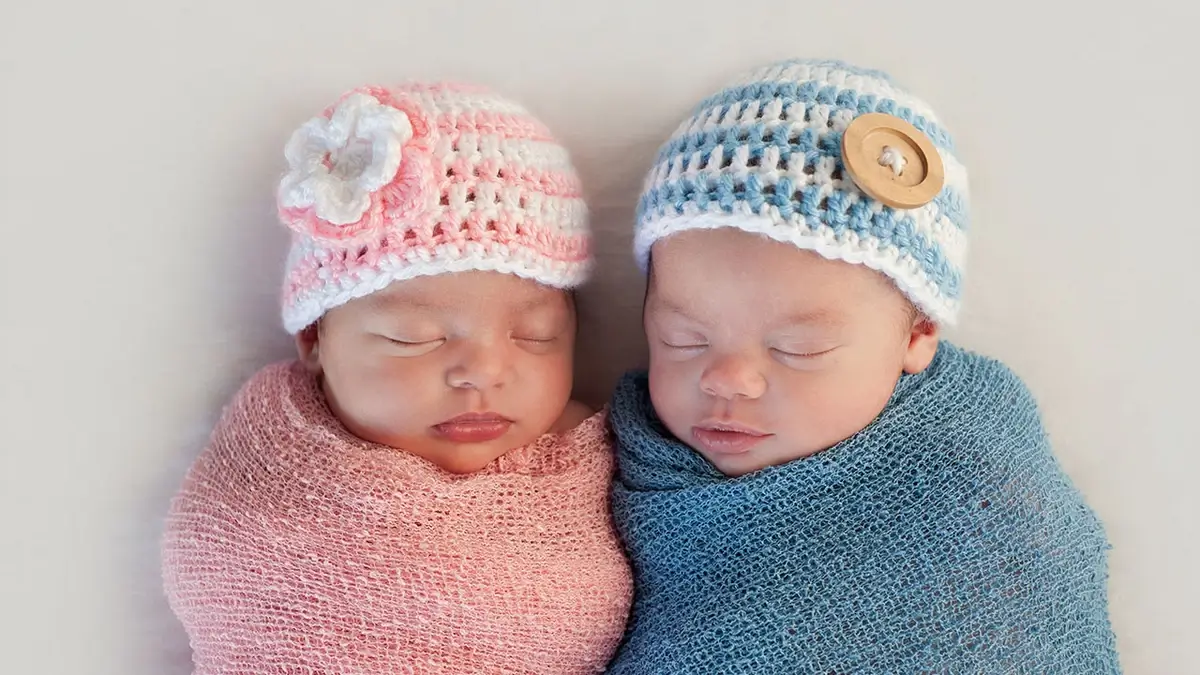

Image: x.com
6. Fraternal Twins Born in Different Years: A Rarity
Fraternal twins born in different years occur when the first is born before midnight on December 31 and the second after midnight on January 1.
This rare event leads to twins having different birth years, a curiosity in birth records.
Such unique timings illustrate the unpredictability of labor and delivery in twins.
These cases offer insights into the timing and dynamics of twin births.
7. Fraternal Twins in Myths and Legends
Romulus and Remus, the founders of Rome in Roman mythology, are among the most renowned fraternal twins.
These legendary figures, raised by a she-wolf, symbolize the power of unity and resilience.
In Yoruba mythology, the Ibeji are revered twin deities, embodying joy and harmony, reflecting the high rate of twin births in Nigeria.
Such myths across cultures emphasize the mystical and societal significance attributed to fraternal twins.
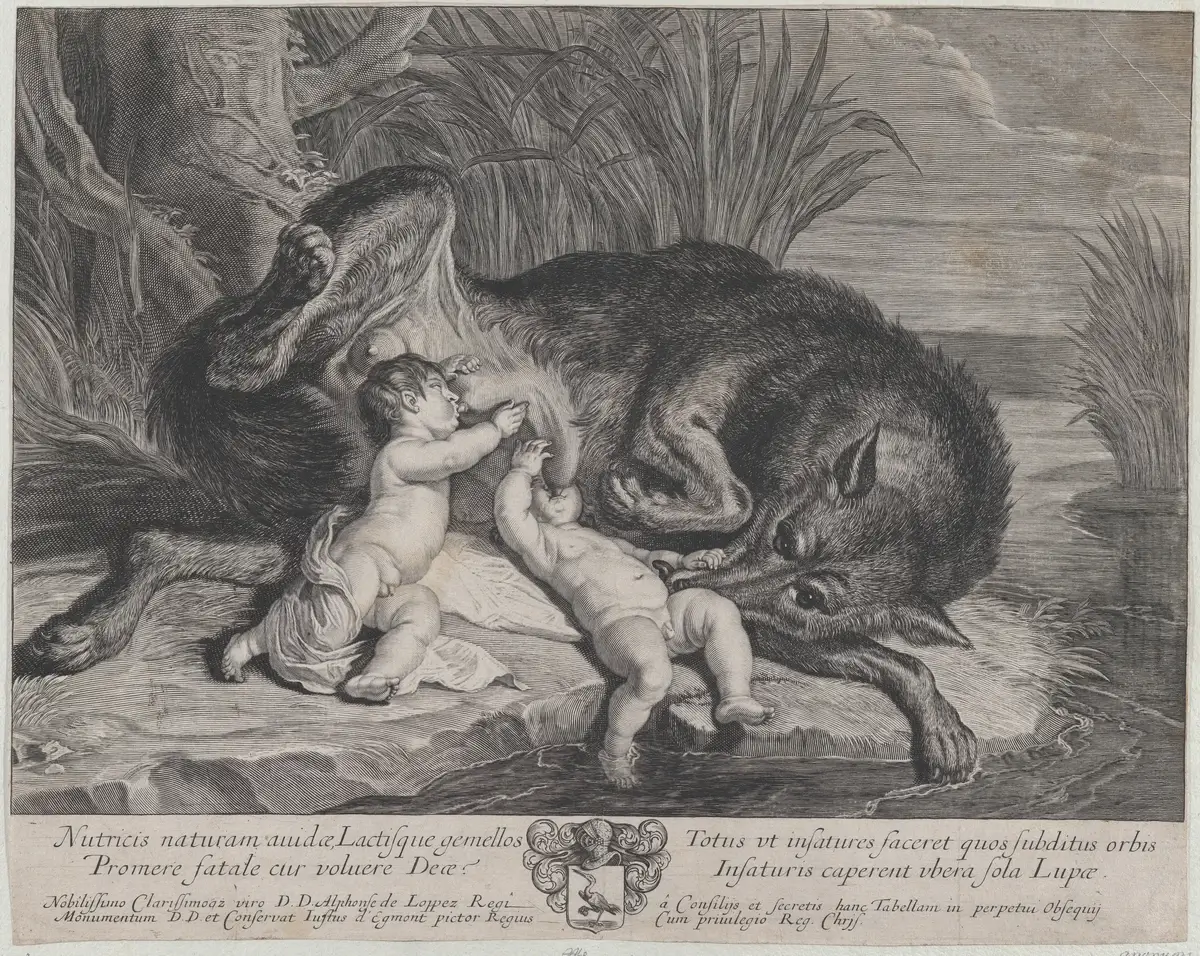

Image: metmuseum.org
8. Genetics vs Environment in Fraternal Twin Development
Fraternal twins’ traits are influenced by both genetics and the environment.
While genetics determine basic characteristics like eye color, environmental factors shape personality and behavior.
Studies on twins separated at birth show significant differences, underscoring the environment’s impact.
Understanding this genetic-environmental interplay is key in developmental psychology and genetics research.
9. Global Trends in Fraternal Twinning Rates
Fraternal twinning rates are highest in Central Africa due to genetic predispositions.
Conversely, East Asia has lower rates, illustrating the impact of genetic diversity.
Nutrition, maternal age, and fertility treatments also affect twinning rates globally.
These trends offer insights into reproductive health and genetic research.
10. Famous Fraternal Twins in the Spotlight
Fraternal twins like Mary-Kate and Ashley Olsen have made significant impacts in entertainment and fashion.
Vin Diesel and his fraternal twin brother highlight differing life paths within twin pairs.
These stories showcase the individuality and achievements of each twin, beyond their shared identity.
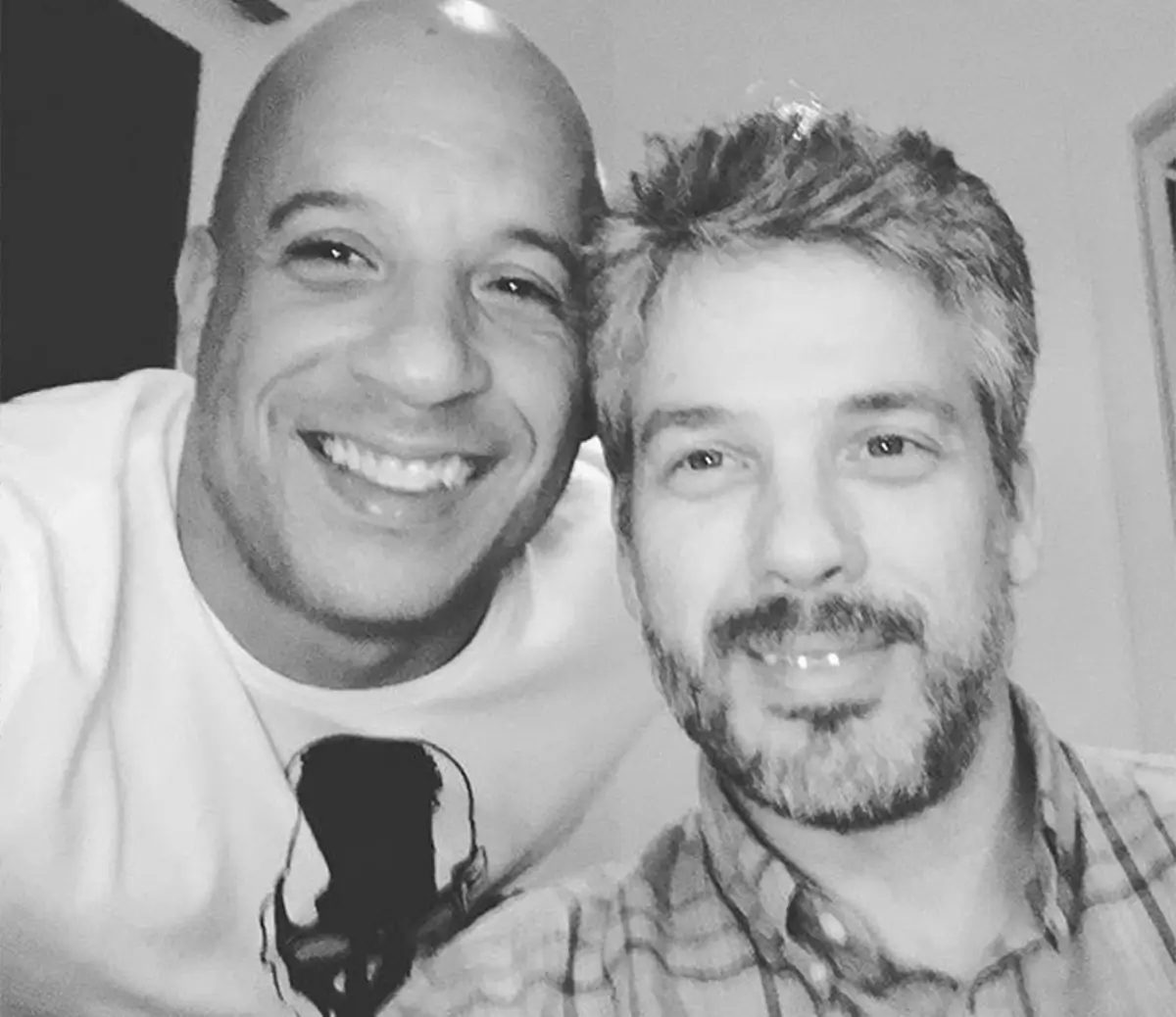

Image: people.com
11. Medical Oddity: Fraternal Twins with Different Dads
Heteropaternal superfecundation results in fraternal twins with different fathers, a rare reproductive phenomenon.
This occurs when a woman ovulates multiple eggs fertilized by sperm from separate encounters.
Such cases are rare but offer unique insights into human fertility and genetics.
They challenge traditional understandings of twin conception and paternity.
12. How Age and Diet Affect Fraternal Twinning
Maternal age influences the likelihood of conceiving fraternal twins.
Women over 35 produce more follicle-stimulating hormone, increasing the chance of releasing multiple eggs.
Dietary factors, like consuming dairy products, also correlate with higher twinning rates.
Studies suggest that these dietary impacts may be linked to growth hormones in foods.
13. Fraternal Twins in Ancient History
Historical records show fraternal twins were both revered and feared in ancient societies.
In some cultures, they were seen as auspicious symbols of fertility and power.
Conversely, other societies viewed twins with suspicion, attributing them with mystical or ominous powers.
These diverse historical perspectives on twins reveal the complex ways humans have interpreted natural phenomena.
14. The Unique Bond of Fraternal Twins
Fraternal twins often develop a deep, emotional connection, despite their genetic differences.
Studies show that this bond is nurtured through shared experiences from early development in the womb to growing up together.
This unique relationship can influence their social and emotional development, often leading to strong empathy and understanding between the twins.
Fraternal twins, like Ashton and Michael Kutcher, illustrate the special dynamic that can exist in such relationships, balancing individuality with a shared bond.
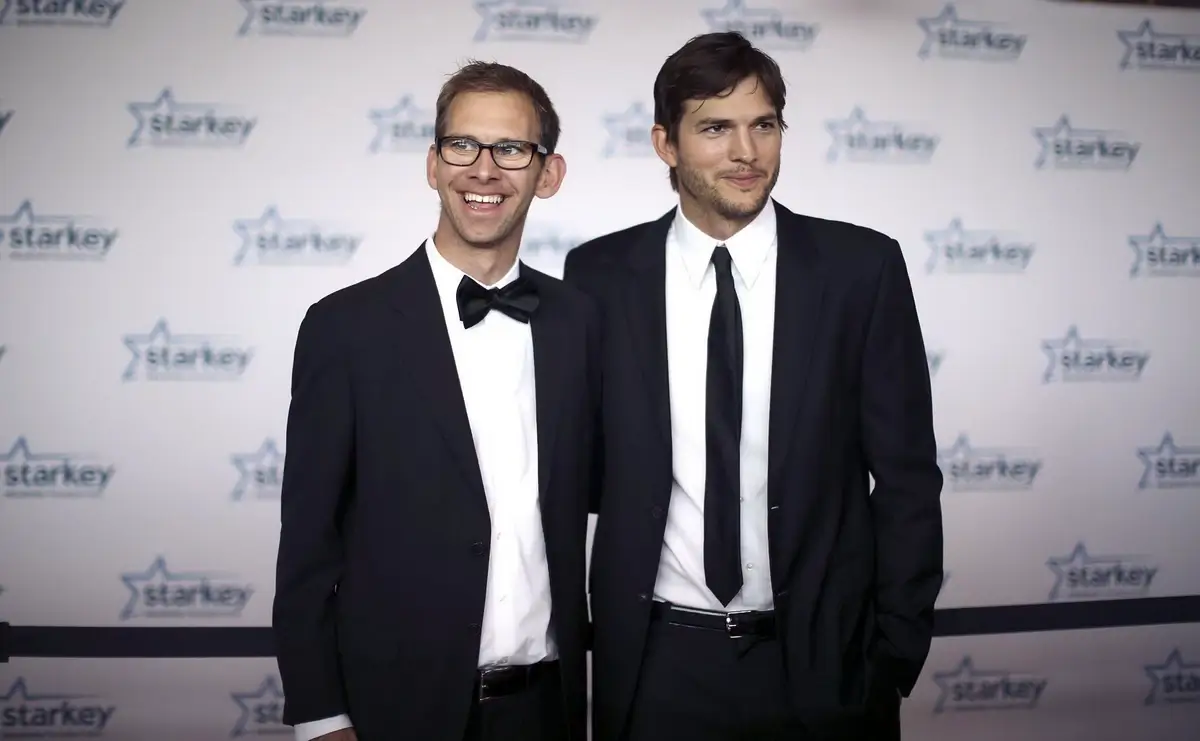

Ashton and Michael Kutcher. Image: CNN
15. Unique Health Profiles of Fraternal Twins
Recent studies have revealed that fraternal twins can have markedly different health profiles, despite being raised in similar environments.
For instance, research has shown that if one fraternal twin develops a non-genetic condition like Type 2 diabetes, the likelihood of the other twin developing it is not significantly higher than in the general population.
This contrasts with identical twins, where if one twin develops such a condition, the likelihood of the other twin developing it is much higher.
These findings are crucial for understanding the complex interaction between genetics and lifestyle in health.
FAQ
What is special about fraternal twins?
Fraternal twins are special because they develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm cells. Unlike identical twins, they are not genetically identical, sharing about 50% of their DNA, similar to regular siblings. This genetic distinction leads to fraternal twins often having different physical appearances, genders, and even blood types, making each twin unique in their own way.
Do fraternal twins know about each other?
Fraternal twins, like all twins, typically develop a strong awareness of each other from a very young age. This awareness is a result of their shared environment and experiences, especially if they grow up together. They tend to be acutely aware of each other’s presence, habits, and behaviors, forming a unique bond that often starts in the womb.
Are fraternal twins 100% related?
Fraternal twins are about 50% genetically related, which is the same genetic similarity that exists between any other siblings born at different times. They are not 100% genetically related like identical twins, who come from the same fertilized egg that splits into two embryos.
Do fraternal twins have a strong bond?
Fraternal twins often have a strong bond, developed through shared experiences and a close upbringing. This bond is similar to the strong relationships seen between siblings, but it can be enhanced by the unique experience of sharing the same age, developmental stages, and often, a close emotional connection from birth.
How rare are fraternal twins?
Fraternal twins are less rare than identical twins. The occurrence of fraternal twins varies globally and is influenced by several factors, including genetics, maternal age, and the use of fertility treatments. In some regions, particularly in Central Africa, fraternal twinning is relatively common, while in other parts of the world, it is less so.
Can fraternal twins feel each other pain?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that fraternal twins can physically feel each other’s pain. However, due to their close emotional bond and empathetic understanding of each other, fraternal twins may be highly attuned to each other’s feelings and discomfort, which can sometimes be misconstrued as feeling each other’s pain.
What traits do fraternal twins share?
Fraternal twins, being genetically similar to regular siblings, can share a variety of traits. These can include physical characteristics like hair and eye color, as well as personality traits. However, the extent of these shared traits can vary greatly, as fraternal twins only share about 50% of their DNA, leading to a wide range of similarities and differences between them.