When we gaze up at the night sky, beyond those glittering stars and the silvery hue of the Milky Way, there’s a bustling universe of satellites silently whizzing around. These unsung heroes, hovering miles above us, shape our modern life in ways most of us rarely ponder.
Whether you’re navigating to a new coffee shop using your phone or binge-watching your favorite series, you have satellites to thank. Ready to delve into some fun facts about satellites? From the fascinating history to the sheer speed of these celestial bodies, we guarantee you’ll be starry-eyed by the end! 🌌
1. The Very First Satellite: A Soviet Sputnik Stunner
Way back in 1957, the world was introduced to its first artificial satellite, named Sputnik 1. This Soviet marvel wasn’t particularly hefty, weighing about 184 pounds, but its launch marked a pivotal moment in space history and sparked the space race between the USA and the USSR.
The satellite emitted beeps that could be received on Earth and was a demonstration of the feasibility of sending robotic spacecraft to other planets. While Sputnik’s life was short-lived (it orbited Earth for only three months), its legacy is monumental.
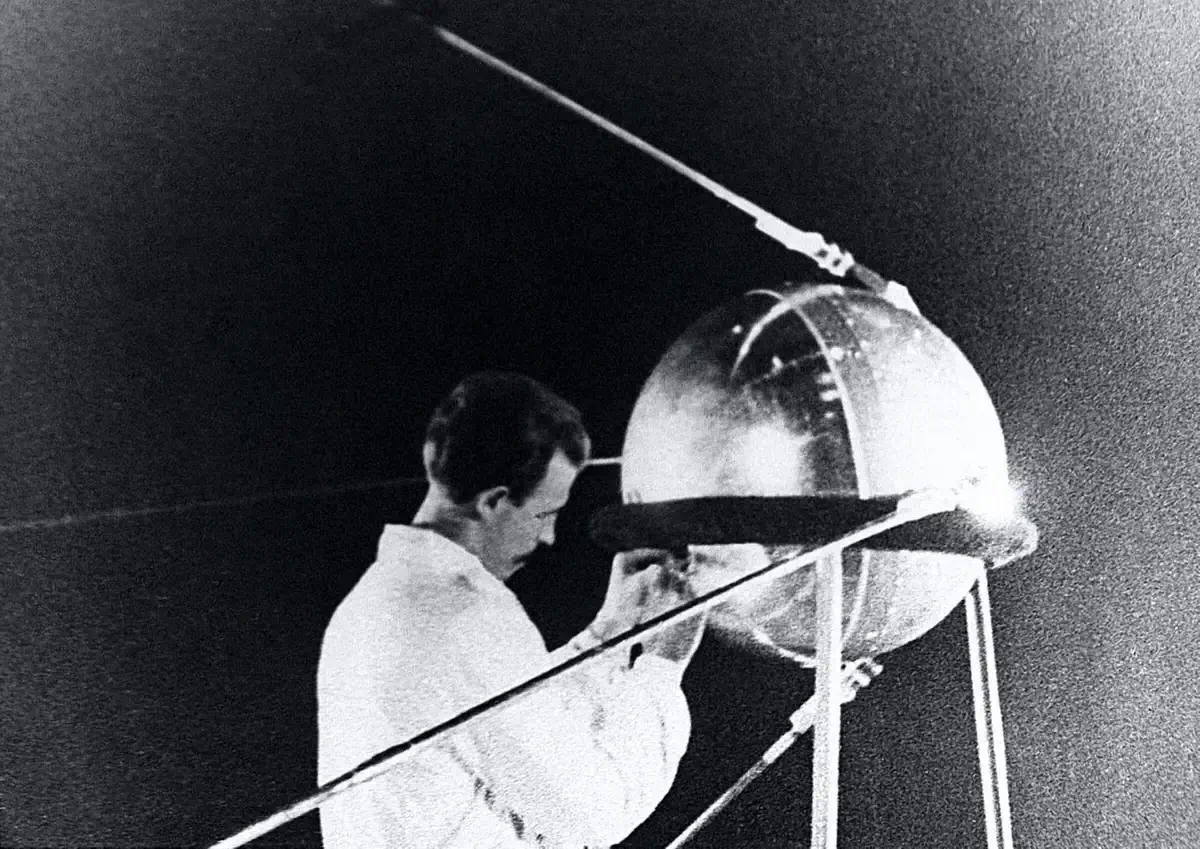

Image source: stylishbag.ru
2. Satellite Speedsters: Orbiting at Thousands of Miles per Hour
Think your sports car is fast? Satellites might just have it beat! These stellar speedsters orbit Earth at mind-boggling speeds. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, for instance, whizz around our planet at speeds of up to 17,500 miles per hour. Yes, you read that right!
This intense speed allows satellites to circumnavigate our planet roughly every 90 minutes. So, while you’re leisurely sipping your morning coffee, there’s a satellite out there that’s completed a full lap around Earth.
3. Not All Satellites are Man-Made: Earth’s Moon, the Original Satellite
Now, here’s an interesting fact! Before humans launched their artificial satellites, Earth already had its own natural satellite – the moon. Yep, that’s right! Our beloved moon, which has been a muse for poets, artists, and lovers for millennia, is technically a satellite.
The moon orbits Earth approximately once every 27.3 days. Its gravitational pull influences our tides, and its phases have served as a calendar for countless civilizations. The next time you admire a full moon, remember, it’s not just a celestial body, but our very own natural satellite.
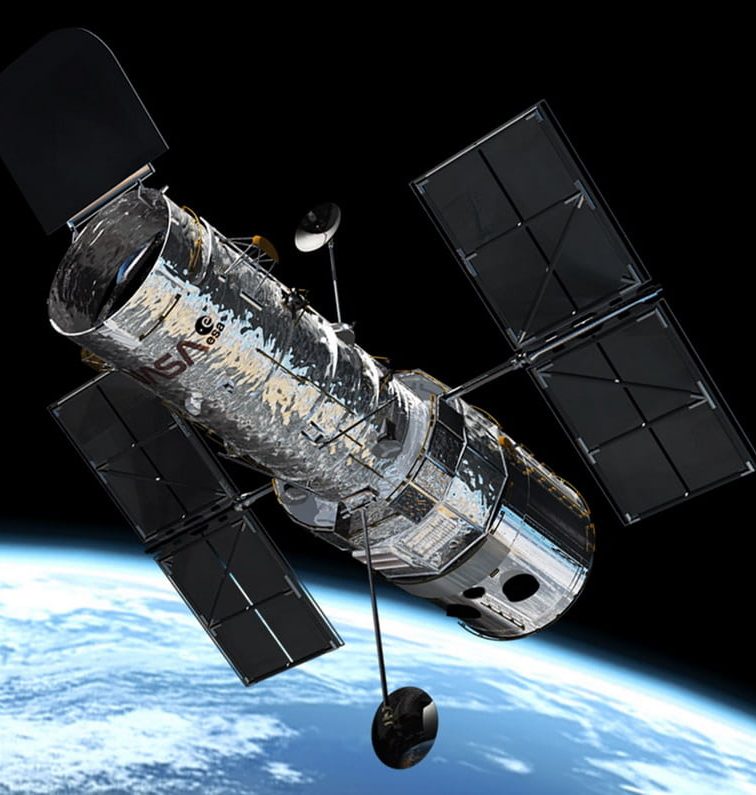
4. Hubble Space Telescope: The Eye in the Sky
When it comes to space observatories, the Hubble Space Telescope reigns supreme. Launched in 1990, this wonder of science has been a game-changer for astronomers. Floating about 340 miles above Earth, it snaps breathtaking photos of our universe, free from atmospheric interference.
What’s more, the Hubble hasn’t just been idly taking pictures; it has transformed our understanding of the cosmos, from tracking storms on Neptune to witnessing distant supernovae. This bad boy even confirmed the existence of black hole powerhouses at the center of galaxies!
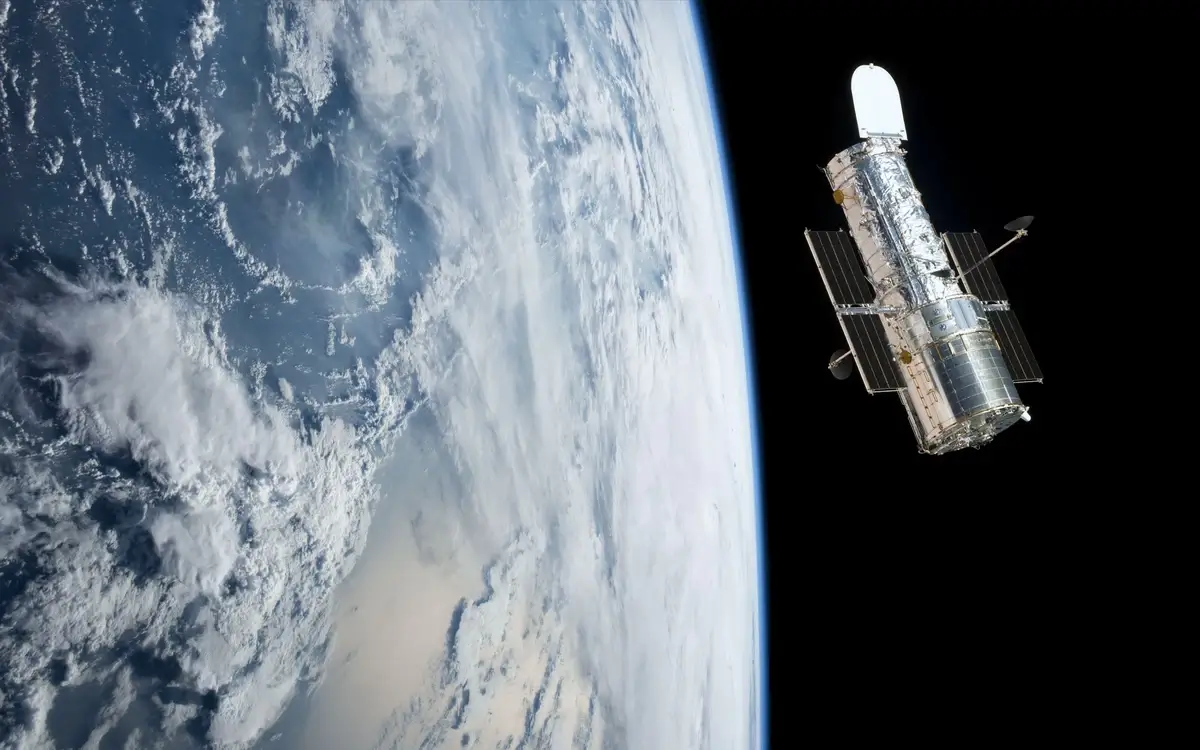

Image source: observatornews.ro
5. Satellites and Space Junk: A Cluttered Space?
While satellites are undoubtedly impressive, they’ve unintentionally created a bit of a mess up there. As they age, many end up as space debris. Today, there are hundreds of thousands of these pieces, some as small as a fleck of paint, zipping around at 17,500 miles per hour!
This space junk poses a real risk to other satellites and the International Space Station. Efforts are underway to develop tech to clean up our space environment because, let’s face it, even the final frontier deserves a good spring cleaning!
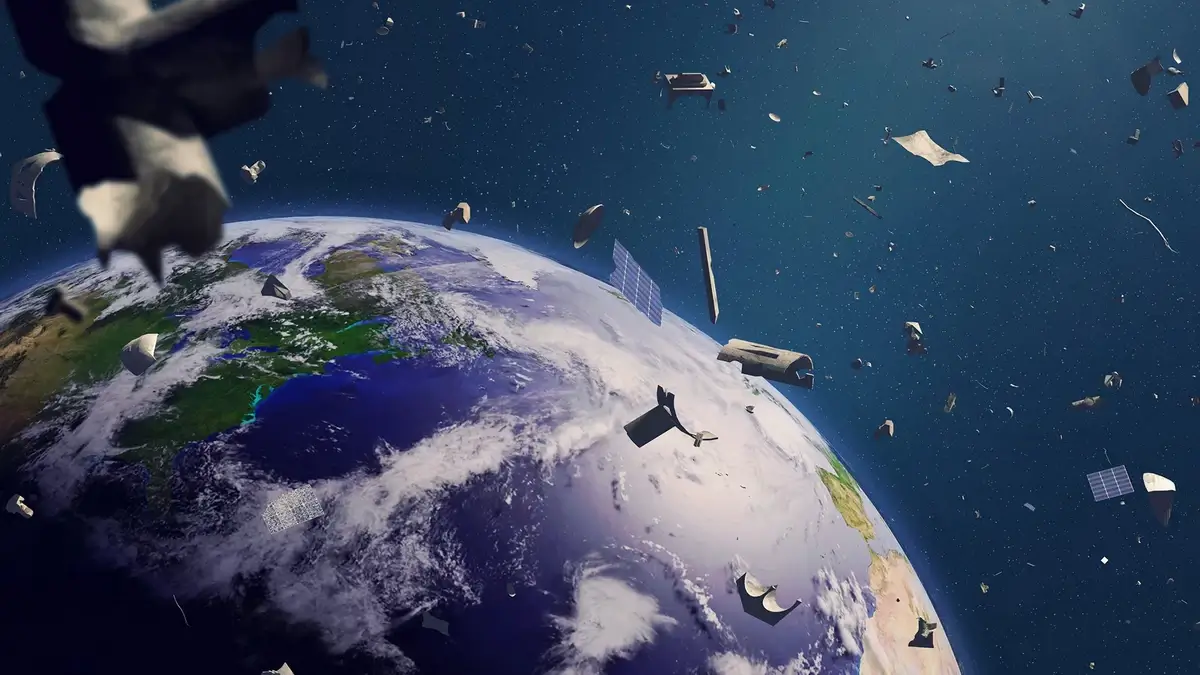

Image source: Britannica
6. Tiny but Mighty: The NanoSat Revolution
Who said size matters? In the world of satellites, small is the new big! Enter NanoSats, miniature satellites weighing between 1-10 kg. Despite their petite stature, these tiny powerhouses perform tasks ranging from weather forecasting to Earth observation.
The real cool fact here is their affordability and quick production time. Universities and startups can now have their own satellite without breaking the bank. It’s safe to say that NanoSats are democratizing space exploration, one mini satellite at a time.
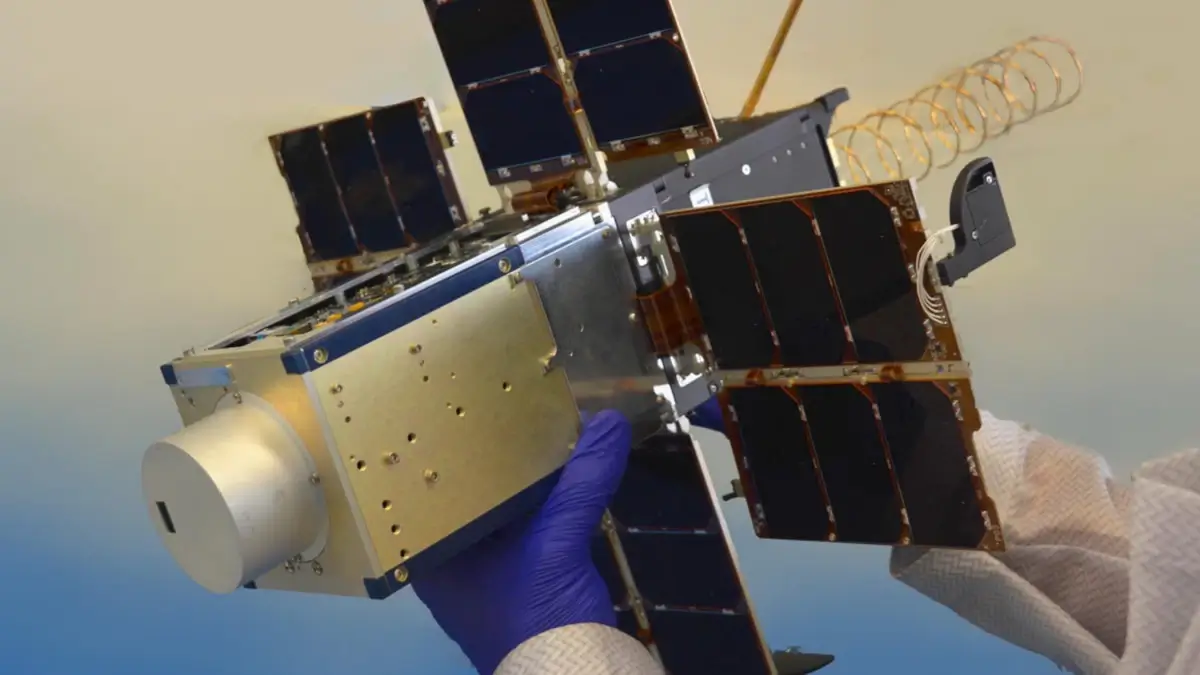

Image source: slashgear.com
7. Communication Kings: The Backbone of Our Global Connectivity
Imagine a world without instant global communication. Sounds tough, right? Thanks to satellite communication, we live in an era where a video call across continents is just a click away. These communication satellites, perched in geostationary orbit, relay signals that power our TV broadcasts, GPS systems, and yes, even some of your favorite mobile apps.
It’s not an exaggeration to say that they’re the unsung heroes behind our digital age. Every time you catch a live international broadcast or get directions to that new sushi place, remember there’s a satellite making it all possible.
8. Starlink’s Satellite Spectacle: Lighting Up the Night Sky
SpaceX’s Starlink project has been turning heads, quite literally! This initiative aims to create a mega-constellation of satellites in space to provide high-speed internet to even the remotest corners of our planet. As of now, thousands of these satellites have been launched, forming a mesmerizing trail in the night sky.
However, it’s not all about internet connectivity. The spectacle of these satellites, moving in a train-like formation, has become an unexpected bonus for stargazers worldwide. But here’s the amazing fact: once operational, Starlink could revolutionize how many people access the digital world.
9. Galileo, GPS, and Glonass: The Triad of Navigation
Ever wondered how your navigation apps are so accurate? Meet the powerful trio: Galileo (EU), GPS (US), and Glonass (Russia). These satellite navigation systems are what make real-time positioning possible, guiding millions around the world daily.
While GPS might be the most well-known, each system has its own fleet of satellites ensuring accuracy and coverage. Together, they form an intricate network that ensures you never really get lost, whether you’re trekking in the Himalayas or navigating the bustling streets of New York.
10. Satellites’ Life Expectancy: Not Immortal After All
Like all good things, satellites, too, have an expiration date. While they achieve marvels, their lifespan ranges from a few years to a couple of decades. Factors determining a satellite’s lifespan include its design, functionality, and, quite interestingly, the amount of fuel it carries.
Once they’ve lived their life, satellites either get nudged into a ‘graveyard’ orbit or, if they’re close enough, burn up upon re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. So, the next time your weather app predicts rain perfectly, remember: that info might be coming from a satellite nearing its retirement!
11. Satellite Sunbathers: Solar Panels in Space
Here’s a cool fact: satellites are avid sunbathers! The vast majority of satellites draw their energy from the Sun using solar panels. These panels convert sunlight into electricity, powering everything from the satellite’s communication instruments to its onboard cameras.
Given that there’s no atmosphere in space to scatter sunlight, satellites get a consistent and powerful dose of solar energy. And while we humans need sunscreen to enjoy the Sun safely, satellites just bask in its glow, harnessing its power to stay alive and operational.
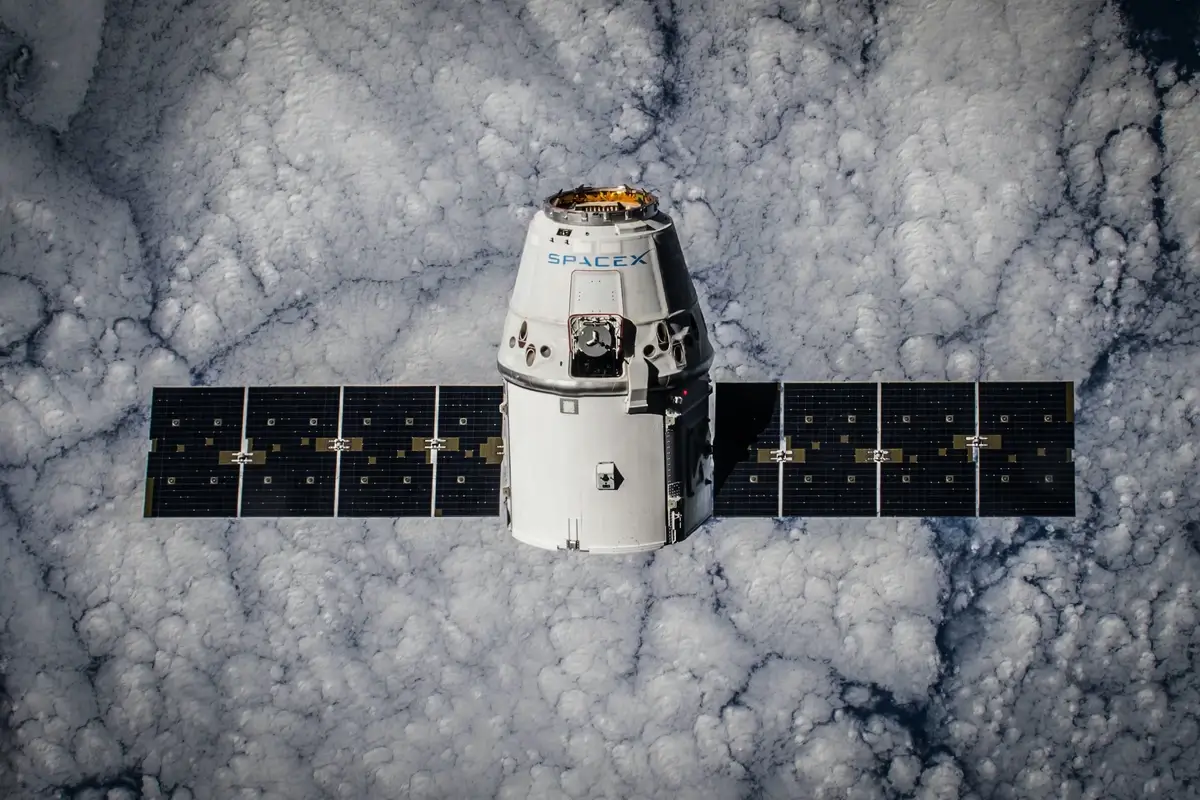

SpaceX / Pexels
12. The Pricey Payloads: The Cost of Launching Satellites
Rocket science doesn’t come cheap, and neither does launching satellites. The price tag attached to sending these hunks of metal into space can run into hundreds of millions of dollars! This hefty cost encompasses the satellite’s construction, rigorous testing, launch vehicle, and ground support operations.
But here’s an interesting fact: recent advancements, like reusable rocket stages and smaller satellites, are gradually making space more affordable. Initiatives like SpaceX’s Falcon 9 are pioneering the charge in cost-effective launches. So, while space remains a premium domain, the doors are slowly opening wider for broader participation.
13. Orbits Galore: From Geostationary to Polar
Not all satellites are in the same dance around Earth. Depending on their purpose, satellites choose different satellite orbits. Geostationary orbits, for instance, keep satellites in a fixed position relative to a point on Earth, making them perfect for communication and broadcasting.
In contrast, polar orbits see satellites circle the Earth in a north-south direction, passing over the poles. This orbit is excellent for Earth observation as it allows the satellite to scan the entire planet. It’s like choosing the perfect lane in a cosmic highway!
14. NASA’s Satellite Science: Studying Earth and Beyond
NASA, often associated with moon landings and Mars rovers, plays a pivotal role in satellite science. Their armada of satellites studies everything from our planet’s climate patterns to the mysteries of deep space.
The cool fact here? Satellites like the Voyager have traveled billions of miles, venturing into interstellar space, sending back invaluable data. Closer to home, Earth-observing satellites provide insights into climate change, hurricanes, and more, proving that NASA’s satellite endeavors span both the intimately close and the impossibly far.
15. A Satellite’s Silent Enemies: Space Weather Hazards
Space isn’t all serene and silent; it’s teeming with radiation storms, solar flares, and charged particles. These elements of space weather pose genuine threats to satellites. A particularly potent solar flare can interfere with a satellite’s electronics, potentially leading to malfunctions or even total failure.
Shielding and protective measures are in place, but the Sun’s unpredictable temperament remains a constant challenge. Just as we on Earth are subject to weather’s whims, satellites too must weather their own kind of stormy days in the cosmic realm.
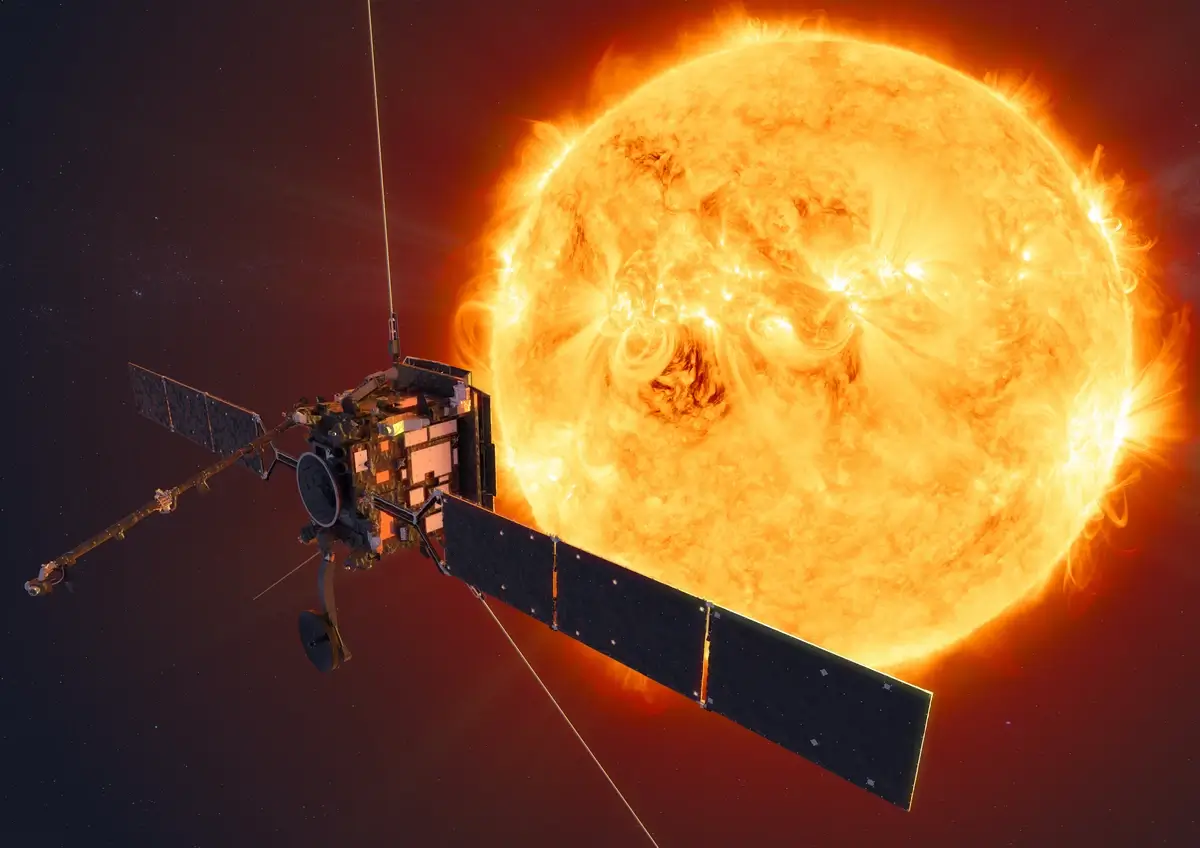

Image source: media4.gmgroup.be
16. From Satellites to Sci-Fi: Inspiring Pop Culture
Satellites, with their high-tech allure, have been a mainstay in pop culture, particularly within the realm of science fiction. Not just as props, but as central elements driving the narrative. Arthur C. Clarke’s 1945 proposal of geostationary satellites is a prime example – what was once sci-fi became a science reality two decades later with the launch of the first communication satellite in such an orbit.
Popular movies like “Gravity” showcase the harrowing threats of space debris, while classics like “GoldenEye” present weaponized satellites. This interesting fact underscores how the creative fantasies of yesteryears can sometimes morph into the technological realities of today.
17. Satellites of Yesteryears: The Vintage Vanguard Collection
The space above us isn’t just filled with state-of-the-art tech; there’s a bit of vintage up there too! Early satellites from the dawn of the space age, like Vanguard 1, the fourth satellite ever launched, still orbit Earth. Launched in 1958, it was an early testament to humanity’s lofty ambitions.
Though these old-timers are no longer operational, they serve as silent reminders of our first forays into space. Like floating museums, they’re artifacts of a time when the very idea of launching something into space was groundbreaking.
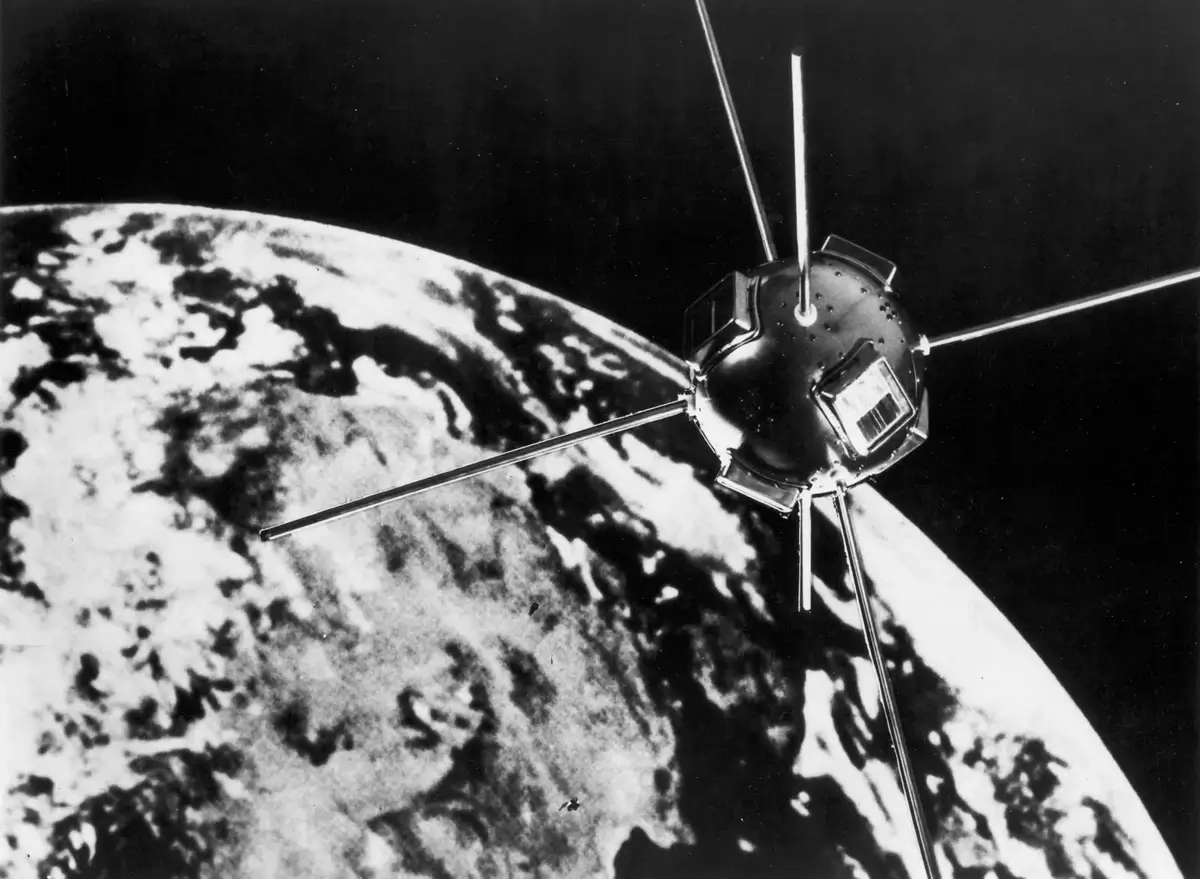

Image source: Britannica
18. Spy in the Sky: Reconnaissance Satellites
The realm of satellites isn’t just about peaceful exploration or global connectivity. Enter the reconnaissance satellites, the real-life “spies” in the sky. For decades, these covert operators have been silently orbiting, gathering intelligence for their respective nations.
An interesting fact? During the Cold War, these satellites played a crucial role in providing intel, helping to keep the delicate balance of power. Their high-resolution cameras and sensors can capture intricate details, making them invaluable assets in the ever-evolving world of espionage.
19. From Space to Your Plate: Satellites and Agriculture
Ever considered how satellites might influence what lands on your dinner plate? Through remote sensing, satellites help farmers monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and even predict pest infestations. This satellite-assisted agriculture ensures better yields and efficient practices.
The next time you savor that perfectly ripe avocado or munch on grains, remember: there’s a chance satellites played a part in bringing that bounty to your table. From space to sustenance, the journey is truly cosmic!
20. Ocean Monitoring Marvels: Keeping Tabs on Our Blue Planet
Our oceans, covering more than 70% of Earth’s surface, are under constant watch from above. Satellites help monitor sea temperatures, track marine life, and even predict tsunamis. Instruments onboard can detect minute changes in sea levels, crucial data for understanding climate change impacts.
These oceanic observations aid in everything from protecting marine biodiversity to ensuring safe sea navigation. So, while the depths of our oceans remain largely mysterious, thanks to satellites, we’re getting a clearer bird’s-eye view of our blue planet’s vastness.
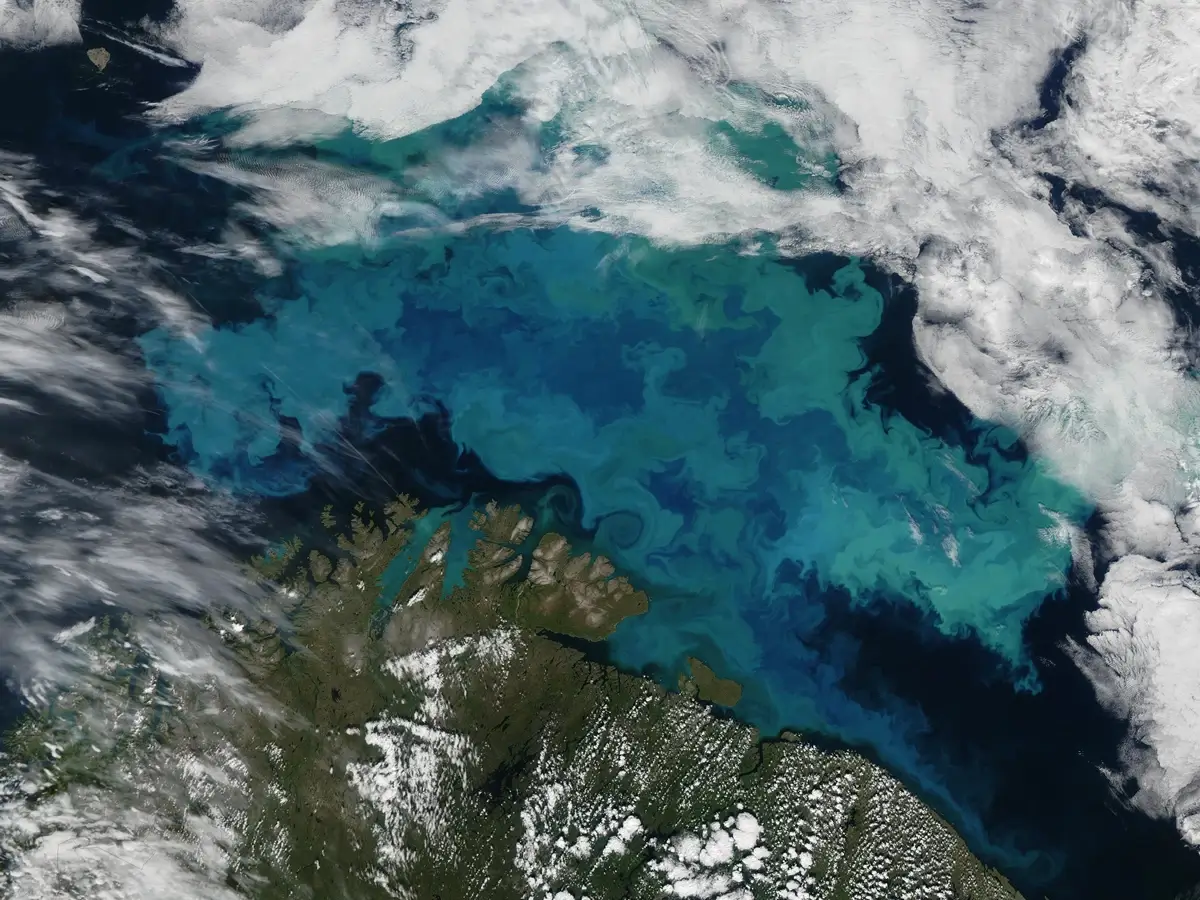

Image source: nsf.gov
FAQ
What Cool Things Do Satellites Do?
Satellites are veritable Swiss Army knives in space. They do a plethora of cool tasks, from snapping high-resolution images of our planet to providing internet in remote areas. Some satellites play detective, tracking hurricanes or monitoring volcanic activities, while others serve as cosmic DJs, relaying TV and radio signals across continents. Plus, let’s not forget those floating navigation aids, helping us find that new café or guiding ships through dense fog.
What Was Unique About the Satellite?
Assuming we’re referencing the very first satellite, Sputnik 1, its uniqueness lay in its trailblazing nature. Launched in 1957 by the Soviet Union, it was humanity’s inaugural attempt to place an artificial object into orbit around Earth. While its design was simple – a metal sphere emitting beeps – it signaled the dawn of the space age, kickstarting the space race between superpowers and opening the door to myriad advancements in satellite technology.
What Are the 3 Main Satellites?
The term “main satellites” can be interpreted in different ways. However, if we’re discussing types based on orbits:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: These are closest to Earth and orbit at altitudes below 2,000 km. They’re often used for Earth observation and telecommunications.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) Satellites: Positioned between LEO and GEO, they typically orbit at altitudes ranging from 2,000 km to 35,786 km. The Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites are in MEO.
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO) Satellites: These orbit at an altitude of around 35,786 km and remain fixed over one spot on the Earth’s equator. They’re commonly used for communication and weather observation.
What Are 5 Uses of Satellites?
- Communication: Satellites enable global broadcasting, telephony, and internet services.
- Earth Observation: They provide crucial data for weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and natural disaster prediction.
- Navigation: Systems like GPS, Galileo, and Glonass rely on satellites to provide global positioning services.
- Space Exploration: Satellites like the Hubble Space Telescope allow us to explore distant galaxies, stars, and planets.
- Military & Intelligence: Reconnaissance satellites gather intelligence, monitor border activities, and support defense operations.
How Fast Do Satellites Travel?
The speed of satellites varies based on their orbit. Satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), for instance, hurtle around our planet at speeds of up to 17,500 miles per hour. This allows them to complete an orbit roughly every 90 minutes. Geostationary satellites, on the other hand, match the Earth’s rotation speed, effectively hovering over one fixed point.
What Are Three Things That Satellites Do for Us?
- Enhancing Connectivity: Satellites play a pivotal role in global communication, be it through television broadcasts, internet connectivity, or international phone calls.
- Guiding Our Way: Through satellite-based navigation systems, we can find our way almost anywhere on the planet, drive through unfamiliar terrains, or sail uncharted waters.
- Monitoring the Environment: Satellites are our eyes in the sky, observing weather patterns, tracking hurricanes, monitoring deforestation, and even gauging the health of marine ecosystems.
Who Owns Satellites?
Satellites can be owned by a variety of entities:
- Governments: Most countries have their own space agencies (like NASA in the US or ESA in Europe) that operate a range of satellites for civilian and defense purposes.
- Private Companies: Firms like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and OneWeb have launched their own satellites, mainly for communication and space exploration.
- International Consortia: Some satellite ventures, especially in communication, are undertaken by international groups to share costs and benefits.
What Country Has the Most Satellites?
The United States holds the record for the highest number of satellites, with a mix of military, commercial, and scientific satellites in orbit. However, it’s essential to note that this number constantly changes as new satellites are launched, and old ones are decommissioned. It’s advisable to check the latest satellite databases or space agency reports for the most current figures.
Who Invented Satellite?
The concept of a man-made satellite has multiple contributors, but one of the earliest visionaries was British science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke. In the 1940s, he conceptualized the geostationary communication satellite, a model widely used today. However, the practical realization of launching the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was achieved by the Soviet Union in 1957.
Why Are Satellites so Important?
Satellites are indispensable for a myriad of reasons. They play a crucial role in global communication, ensuring we stay connected, no matter how remote our location. Their continuous monitoring of Earth provides invaluable data on weather, climate change, and potential natural disasters. In navigation, they ensure we never lose our way. Furthermore, they play a significant role in scientific advancements, from understanding our own planet better to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos. In essence, satellites are the unsung heroes that silently stitch our modern world together.