In the intricate web of nature, the seemingly simple question of what animals eat crickets unfolds a fascinating tapestry of predators and prey. Crickets, often heard but seldom seen, are more than just background noise in our gardens and fields. They are a vital part of the ecosystem, serving as a key food source for a diverse array of animals.
From the stealthy leap of a frog to the precise pounce of a bearded dragon, the pursuit of these chirping insects is a tale of survival and adaptation. In this exploration, we’ll dive into the varied world of cricket predators, revealing how these small insects play a monumental role in the diets of creatures big and small.
Join us on a journey through different habitats, from the dense underbrush to the comfort of our homes, as we uncover the myriad of animals for whom crickets are not just a sound, but a staple.
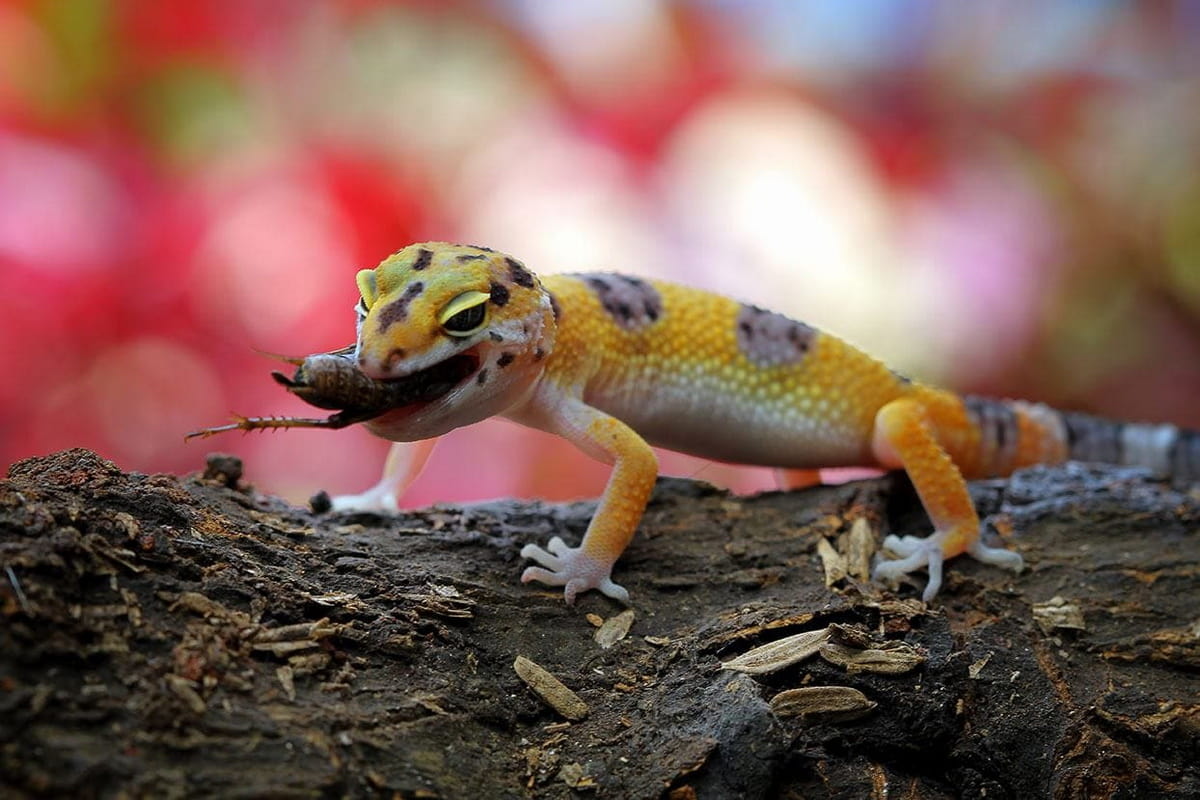
Reptiles That Eat Crickets
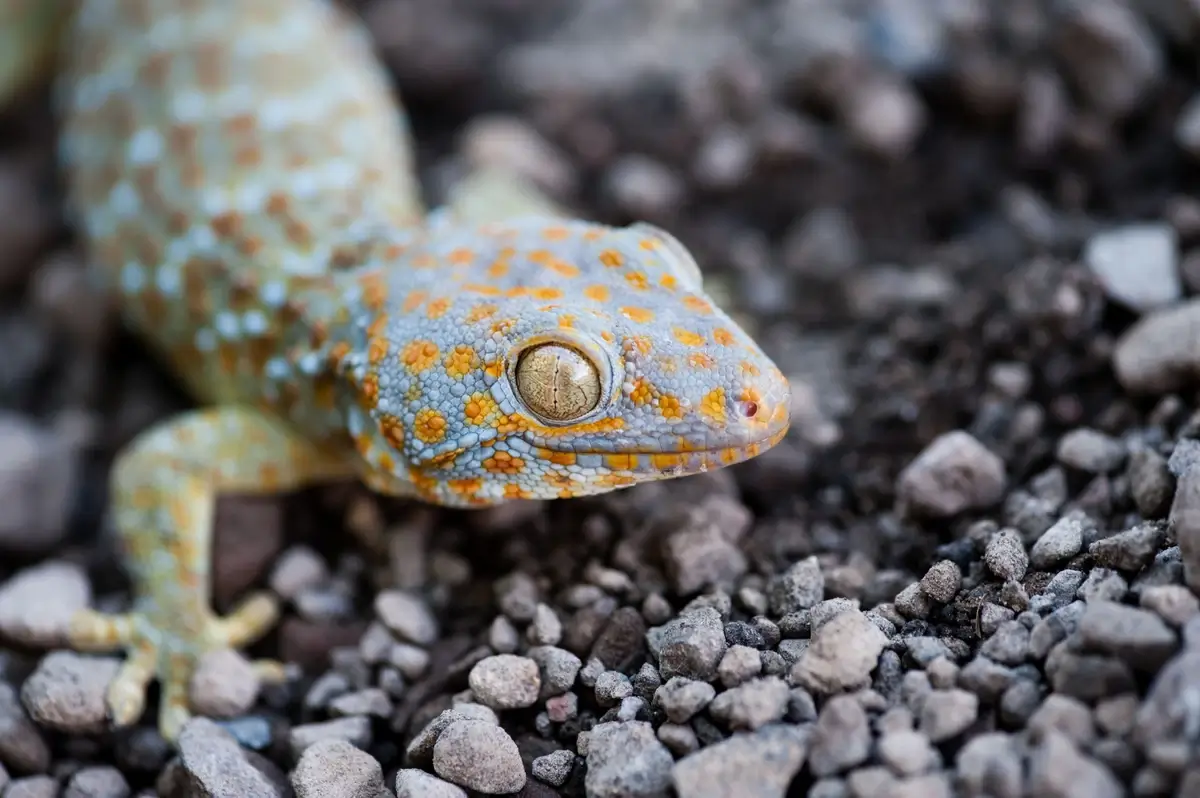

Image: thesprucepets.com
Reptiles are known for their varied diets, and many of them include crickets as a significant part of their nutrition. Here’s a look at some of the reptiles that commonly consume crickets:
- Bearded Dragons: Bearded dragons are among the most popular pet reptiles and have a diet that includes both plant matter and insect protein. Crickets are an ideal food choice for them because they are nutritious and stimulate the dragons’ hunting behavior. These reptiles benefit from the protein, calcium, and other nutrients provided by crickets.
- Leopard Geckos: Leopard geckos are strictly insectivorous, meaning they survive on a diet of insects alone. Crickets serve as an excellent food source for leopard geckos, offering vital nutrients and the opportunity for natural hunting activity.
- Crested Geckos: Typically small in size, crested geckos in the wild mainly consume plant material with occasional insects. In captivity, they require supplemental insects for optimal health, and crickets are a suitable addition to their diet.
- Veiled Chameleons: These reptiles are not the easiest to care for due to their sensitivity to environmental changes. However, their diet is relatively simple, primarily consisting of insects like crickets. They use their long, sticky tongues to skillfully catch crickets.
- Tokay Geckos: Known for their striking appearance, tokay geckos are opportunistic carnivores that feed on insects, including crickets. These geckos enjoy the mental and physical stimulation that comes from hunting crickets.
- Chinese Water Dragons: These reptiles are good alternatives to iguanas for people with limited space. They are adept climbers and use vertical space in their enclosures to hunt for food like crickets.
- Green Anoles: Small in size, green anoles primarily consume insects. Crickets are a great food option for them, providing necessary nutrients in a form that stimulates their natural predatory behaviors.
- Tortoises: Some species of tortoises are omnivores and will include small animals like crickets in their diet. They typically catch crickets with the sharp edges of their beak and consume them whole or in small pieces.
- Iguanas and Garter Snakes: These reptiles also include crickets in their diet. Iguanas, for instance, are omnivorous and may consume crickets along with plant material. Garter snakes, on the other hand, are known to eat a variety of prey, including crickets, which are easy for them to digest and offer hydration benefits.
Crickets are not only a source of protein but also provide essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious addition to the diets of these reptiles. It’s important to note that when feeding crickets to reptiles, they should be ‘gut loaded’, meaning the crickets are fed a nutritious diet before being offered to the reptile. This process enhances the nutritional value of the crickets, making them even more beneficial for the reptiles’ health.
Amphibians That Eat Crickets
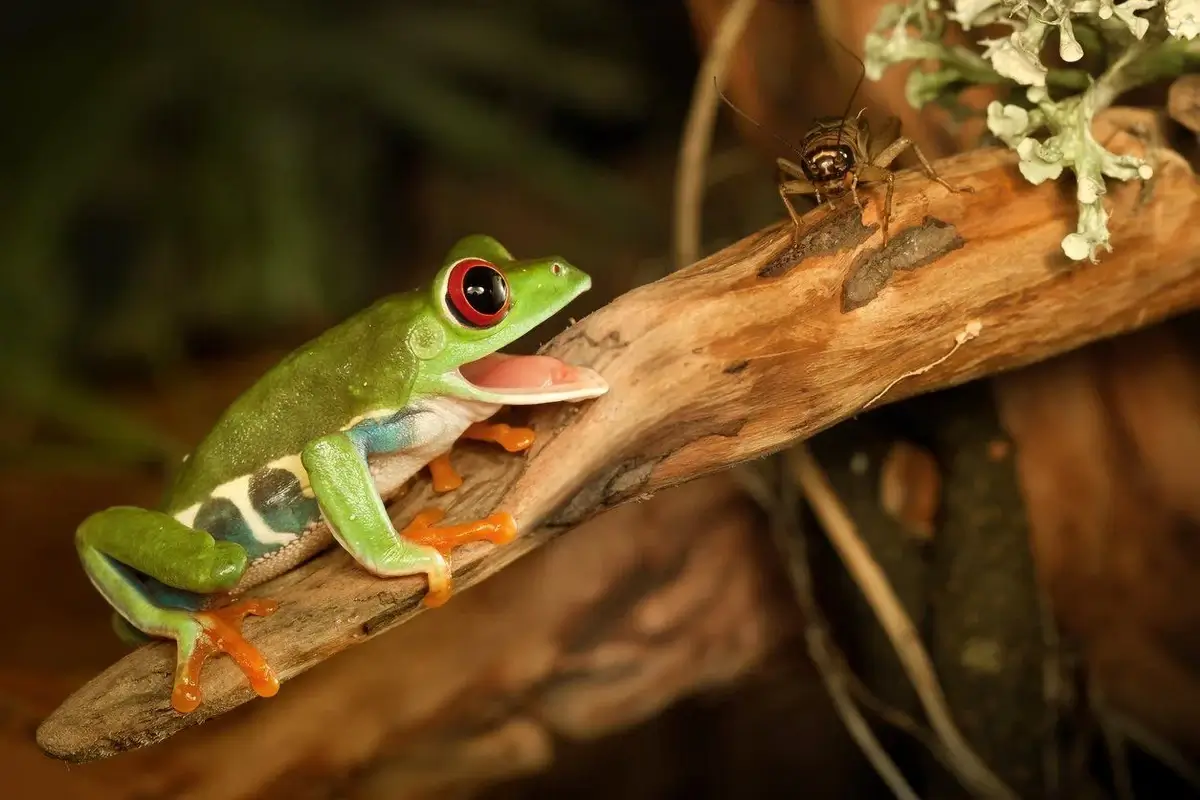

Image: thebuginator.com
Amphibians are diverse in their dietary habits, and many species include crickets as a part of their diet. Here’s a look at some amphibian species that commonly consume crickets:
- Salamanders: Salamanders, both in their juvenile and adult stages, are carnivorous and consume a variety of small insects and invertebrates, including crickets. They have a diet that can consist of flies, mosquito larvae, isopods, and smaller crickets, sometimes referred to as “pinhead” crickets. Their diet changes slightly as they grow, but crickets remain a staple due to their high protein content.
- Frogs and Toads: Many species of frogs and toads also feed on crickets. Crickets serve as a significant source of protein for these amphibians, which is essential for their growth and development. The diet of frogs and toads can also include other insects like mealworms and wax worms, but crickets are particularly favored due to their size and nutritional value.
In terms of feeding practices, it’s important to consider the size of the crickets in relation to the size of the amphibian. Juvenile amphibians typically require smaller crickets, while adults can handle larger ones. The nutritional content of the crickets can be enhanced by gut-loading them before feeding. This involves feeding the crickets a nutritious diet so they are loaded with vitamins and minerals beneficial for the amphibians.
Birds That Eat Crickets

Image: richardjacksonsgarden.co.uk
Birds play a crucial role in various ecosystems, and many bird species include crickets in their diets. Here are some notable examples:
- Robins: Robins are common ground foragers known for their ability to catch crickets by hopping along the ground and listening for the movement of insects. They quickly pounce and grab crickets with their beaks.
- Sparrows: Sparrows, including Song Sparrows and Fox Sparrows, forage on the ground and use their feet to uncover hidden insects like crickets. Insects form a significant part of their diet, especially during the breeding season.
- Starlings: These adaptable birds have a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, and seeds. Starlings often forage in large flocks and are known to consume a wide variety of insects, including crickets.
- Pheasants: These large, ground-dwelling birds feed on insects, seeds, and fruits. During the breeding season, when they need more protein, they are known to eat crickets. Pheasants feed on crickets found on the ground and can catch them in mid-air.
- Bluebirds, Sparrows, Chickadees, Quails: These birds also consume crickets, hunting them on the ground or catching them in mid-air.
Crickets provide these birds with essential nutrients like protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. They are a particularly valuable food source during the breeding season, aiding in the growth and development of birds. Their consumption of crickets also plays a significant role in controlling cricket populations, maintaining balance in the ecosystem, and serving as a natural form of pest control.
Mammals That Eat Crickets

Oli R / Flickr
A variety of mammals include crickets in their diets due to the nutritional benefits these insects provide. Here are some of the common mammal species known to consume crickets:
- Hedgehogs: These spiky mammals are highly insectivorous. Their diet may include a range of insects such as beetles, caterpillars, grasshoppers, millipedes, termites, moths, and crickets. Hedgehogs use their well-developed senses of hearing and smell to locate their prey, and their curved claws are well-suited for digging in search of insects.
- Shrews and Tenrecs: Shrews, which are found almost globally, have a high metabolic rate and must consume large amounts of insects often. Tenrecs, native to Madagascar, also primarily eat insects and their larvae. These small mammals belong to the previously recognized order Insectivora, which included insect-eating mammals.
- Anteaters, Armadillos, and Aardvarks: These creatures, found in the Americas (anteaters and armadillos) and Africa (aardvarks), are insectivores with a particular taste for ants, termites, and crickets. They use their long, sticky tongues and strong front claws to dig for and capture their prey.
- Omnivorous Mammals: Certain omnivorous mammals also include insects like crickets in their diet. This group includes species like black bears, coatimundis, and opossums. Though insects form a small part of their diet, they are an essential source of protein and other nutrients.
Crickets offer numerous nutritional benefits to these mammals, including high protein content, essential amino acids, calcium, iron, vitamins like B12 and thiamine, and other minerals. These nutrients are crucial for muscle growth, repair, and overall health and well-being of these mammals.
In their natural habitats, these mammals employ various techniques to hunt and consume crickets, from using acute sensory abilities to detect and capture them on the ground to catching them in mid-air.
Insects and Arachnids That Eat Crickets

Image: macrocritters.wordpress.com
In the realm of insects and arachnids, several species are known to prey on crickets. Here are some of the notable ones:
- Spiders: Many spider species, including tarantulas, are known to consume crickets. They use various hunting strategies, such as web-spinning and camouflage, to capture their prey. Spiders prefer live prey and utilize their fangs to immobilize and consume crickets. It’s important to feed spiders clean crickets, free from pesticides and parasites, to ensure their health. Crickets serve as a nutritious meal for spiders, providing them with essential protein and other nutrients necessary for their growth and overall health.
- Praying Mantises: Praying mantises are skilled hunters known for their spine-covered front legs, which they use to capture prey like crickets. They are particularly effective due to their camouflage abilities, giving them an advantage in hunting. Mantises prefer live prey and will only eat crickets they have caught or hunted themselves.
- Ground Beetles and Wasps: Other insect predators of crickets include ground beetles and wasps. These predators play a crucial role in controlling cricket populations in various ecosystems.
- Ants: Some ant species also prey on crickets. They are effective in reducing cricket populations due to their social hunting strategies and large numbers.
These insects and arachnids contribute significantly to the balance of ecosystems by controlling cricket populations. Their predatory behaviors not only demonstrate the complexity of food chains but also the importance of each species in maintaining ecological harmony. As natural predators, these creatures help regulate cricket numbers, preventing overpopulation and the associated issues. In turn, the crickets provide a valuable food source for these predators, playing a crucial role in their nutritional intake and survival.
Aquatic Animals That Eat Crickets

Image: Reddit
In the aquatic world, several species are known to include crickets in their diet. This dietary choice is often seen in both freshwater and marine environments.
- Cichlid Fish: Cichlid fish, known for their diverse diet, can eat crickets as a part of their feeding routine. It’s recommended to feed crickets to cichlid fish once or twice a week as a supplement to their diet. Crickets provide them with a high-protein diet and stimulate their predatory instincts. However, care should be taken to avoid overfeeding and to choose crickets of appropriate size to prevent choking hazards.
- Turtles: Many common household pet turtles, including Box Turtles, Red-Eared Sliders, and Painted Turtles, are omnivorous and can consume crickets. Crickets serve as a nutritious snack and are an excellent protein source for turtles. However, it’s important to feed them in limited amounts due to their low calcium-to-phosphorus ratio and to ensure they are gut-loaded with a high-calcium feed before feeding.
- Betta Fish and T-Bar Cichlids: Betta fish, native to Southeast Asia, and T-bar cichlids are also known to eat crickets. Betta fish in particular, due to their insectivorous nature in the wild, can be trained to eat crickets in aquarium settings. Crickets can be a good source of protein for these fish, supplementing their regular diet.
- Other Fish Species: While not all fish will eat crickets, some species like killifish and certain species of cichlids may include crickets in their diet. Crickets provide essential nutrients for these fish and can be a part of a balanced and varied diet. It’s crucial to source high-quality crickets and prepare them properly by gut-loading and ensuring they are free from parasites and bacteria before feeding them to fish.
In conclusion, crickets can be a nutritious and beneficial food source for various aquatic animals, particularly certain fish species and turtles. However, it’s important to understand the specific dietary needs and preferences of each species and to prepare crickets properly to ensure their safety and nutritional value.
Conclusion
The question “what animals eat crickets” reveals a vast network of wildlife, spanning from land to water. This small insect is a crucial dietary element for various reptiles, amphibians, birds, mammals, and even fellow invertebrates like spiders.
Each of these creatures relies on crickets for essential nutrients, playing a vital role in their survival and the ecological balance. This intricate interdependence highlights the importance of every species, no matter how small, in maintaining the biodiversity of our ecosystems.
FAQ
What are the best pets that eat crickets?
Some of the best pets that eat crickets include bearded dragons, leopard geckos, and crested geckos. These reptiles rely on crickets as a primary source of protein. Birds like chickens can also consume crickets. Amphibians, such as frogs and toads, are natural predators of crickets. These pets not only benefit nutritionally from eating crickets but often enjoy the process of hunting them, which can provide mental and physical stimulation.
What are 3 organisms that eat crickets?
Three common organisms that eat crickets include:
- Frogs and Toads: They consume crickets as a significant part of their diet, especially in their adult stages.
- Spiders: Many spider species, particularly the larger ones like tarantulas, prey on crickets.
- Birds: Several bird species, particularly those that are insectivorous, feed on crickets as a part of their diet.
What are crickets natural enemies?
Crickets have several natural enemies, which include:
- Amphibians: Such as frogs and toads, which consume crickets as part of their diet.
- Reptiles: Lizards and some snake species are known to prey on crickets.
- Birds: Insectivorous birds often feed on crickets.
- Insects and Arachnids: Various species of spiders, ground beetles, and even other larger or carnivorous insects can be predators of crickets.
- Mammals: Small mammals like shrews and bats may also feed on crickets.