Puget Sound, a mesmerizing marine gem in the heart of Washington State, is brimming with fascinating facts.
Formed by the retreat of the Vashon Glacier around 15,000 years ago, it spans an area of about 1,020 square miles and reaches depths of approximately 930 feet near Point Jefferson.
Named after Peter Puget, a lieutenant in George Vancouver’s 1792 expedition, this complex estuarine system supports a rich tapestry of life, with over 3,000 species calling it home.
From its historical significance to its ecological wonders, Puget Sound is not just a body of water but a living, breathing testament to nature’s marvels.
1. Origins of Puget Sound’s Name
Puget Sound was named in 1792 by British explorer George Vancouver in honor of his officer, Lieutenant Peter Puget.
This occurred during an expedition to chart the Pacific Northwest, a pivotal moment in maritime history.
This naming not only anchored the region in European maps but also marked the beginning of its global recognition.
The choice of name reflects the era’s practices of exploration and discovery, solidifying Puget’s legacy in the region’s identity.
2. Deepest Point of Puget Sound
The deepest point of Puget Sound, near Point Jefferson, reaches a staggering depth of about 930 feet (283 meters).
This depth, significant in its contrast to the sound’s average of 450 feet, is a result of glacial carving from the last Ice Age.
The deep basins created are crucial for the local marine ecosystem, affecting everything from nutrient cycles to habitat diversity.
These depths provide a hidden world that is key to understanding the sound’s ecological balance.
3. Marine Biodiversity in Puget Sound
Puget Sound’s marine biodiversity is a rich tapestry, housing over 3,000 species.
This includes 200 species of fish, 100 species of birds, and numerous marine mammals like orcas and seals.
Its diverse habitats, from shallow eelgrass meadows to deep basins, create a mosaic of life.
Key species like the Chinook salmon are not only ecologically vital but also culturally significant to the local indigenous communities.
This biodiversity underscores the sound’s role as a crucial ecological hub in the Pacific Northwest.
4. Puget Sound’s Glacial History
The glacial history of Puget Sound is a narrative of transformation. About 15,000 years ago, the Vashon Glacier sculpted the sound’s current form.
This immense glacier, part of the last Ice Age, was responsible for carving out the deep basins and depositing rich sediments that now support the sound’s diverse habitats.
The retreat of this glacier was a pivotal event, shaping not just the geography but also the subsequent ecological development of the region, laying the groundwork for its rich marine life.
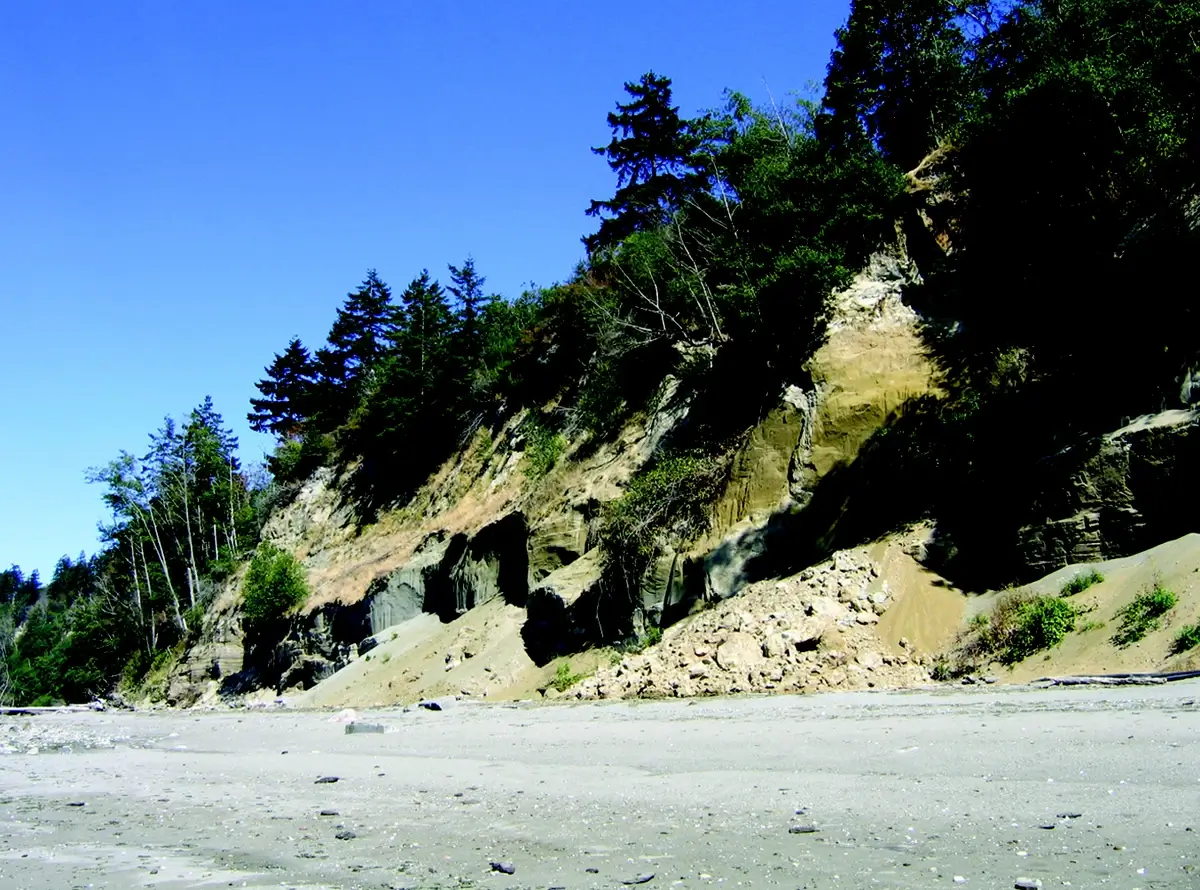

Image: eopugetsound.org
5. Home of the Giant Pacific Octopus
Puget Sound is renowned as the habitat of the Giant Pacific Octopus, the largest octopus species in the world.
These magnificent creatures can weigh up to 600 pounds and have an arm span of up to 20 feet.
They are known for their intelligence, ability to camouflage, and unique hunting strategies.
This species plays a vital role in the marine ecosystem of Puget Sound, balancing the underwater food web.
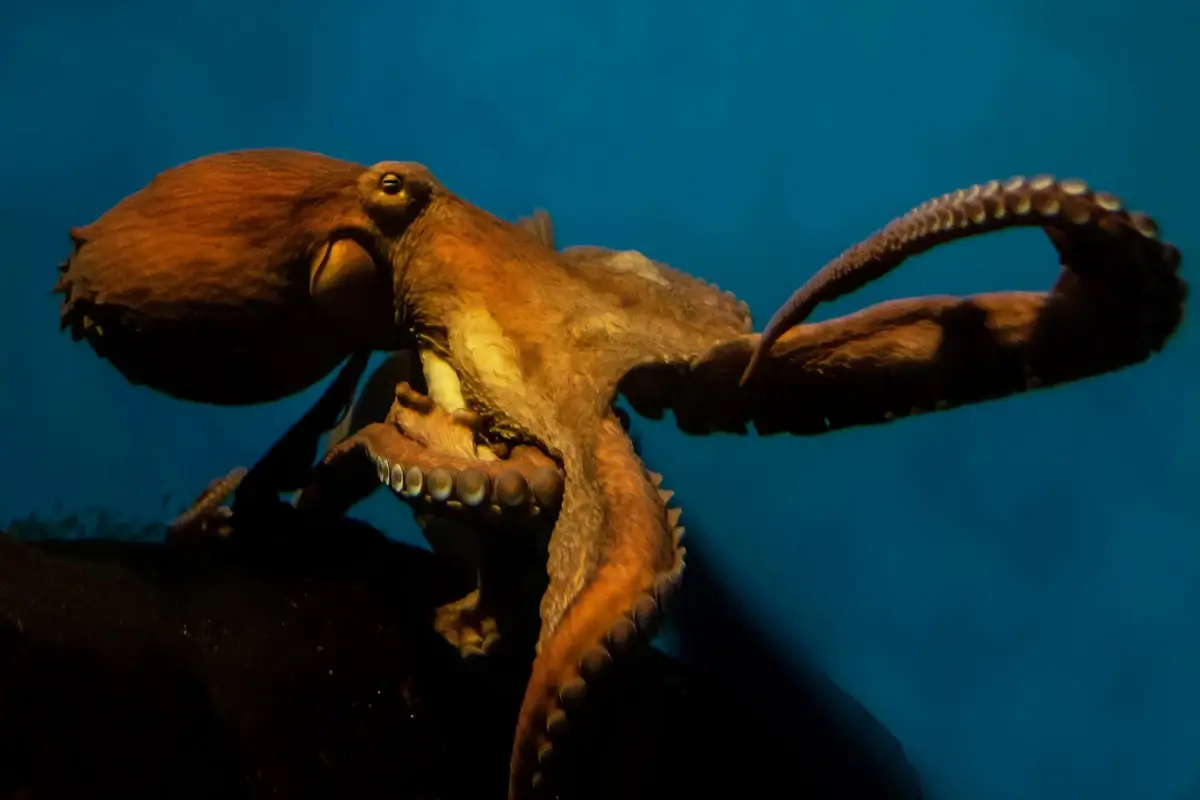

Image: americanoceans.org
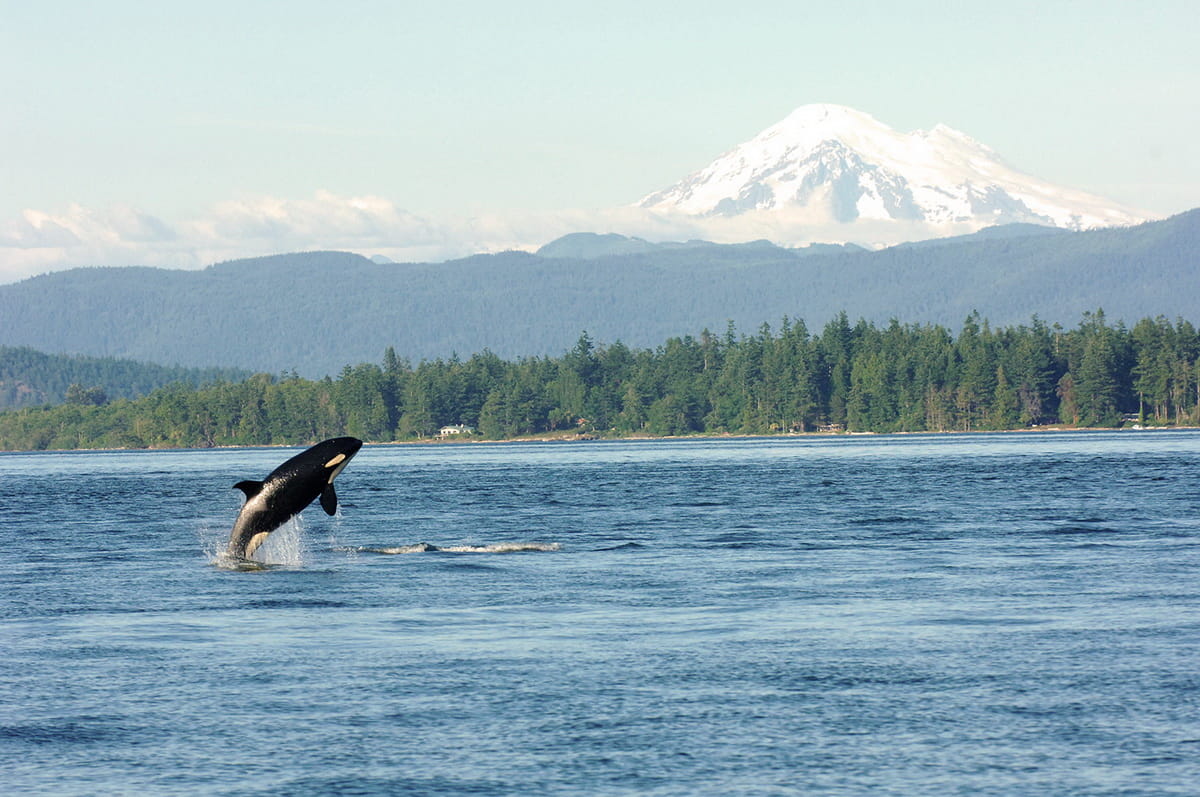
6. Unique Orca Populations in Puget Sound
Puget Sound is home to a distinct population of orcas, known as the Southern Resident Killer Whales.
These orcas are unique due to their diet, which primarily consists of Chinook salmon, and their complex social structures.
They are an iconic symbol of Puget Sound and hold significant cultural value to the local communities.
Conservation efforts are crucial for these orcas, as they are currently listed as endangered due to threats like pollution and declining salmon populations.
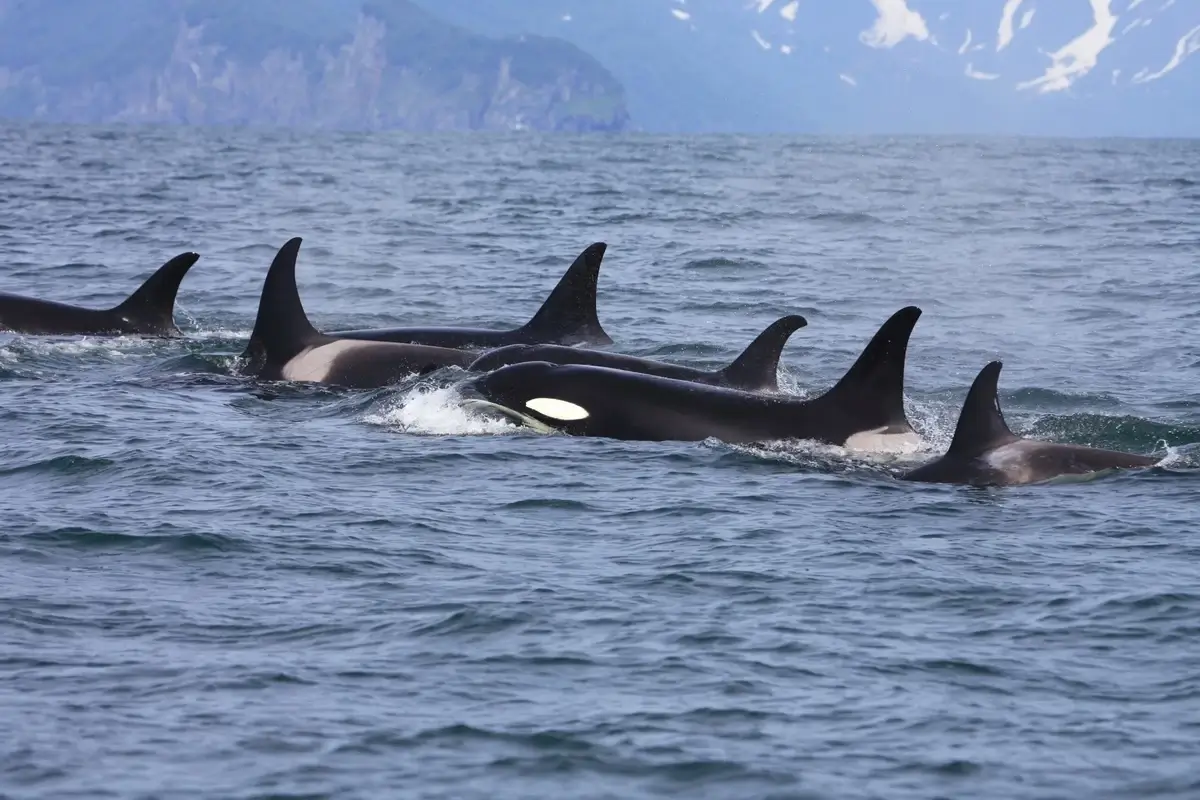

Image: earthjustice.org
7. Historical Shipwrecks in Puget Sound
Puget Sound’s waters hide numerous historical shipwrecks, each with its own story.
These wrecks include vessels from the 19th and 20th centuries, reflecting the region’s rich maritime history.
Among them is the famous SS Governor, a passenger steamer that sank in 1921 after a collision.
These underwater sites are not only historical artifacts but also serve as artificial reefs, supporting diverse marine life.
8. The Salmon Runs of Puget Sound
The salmon runs in Puget Sound are an annual ecological phenomenon, crucial for the local ecosystem.
Millions of salmon, primarily Chinook and Coho, migrate from the ocean to their natal rivers to spawn.
This migration is vital for the regional food web, supporting species like orcas and bears, as well as local fishing industries.
The health of these salmon runs is an indicator of the overall health of Puget Sound’s ecosystem.
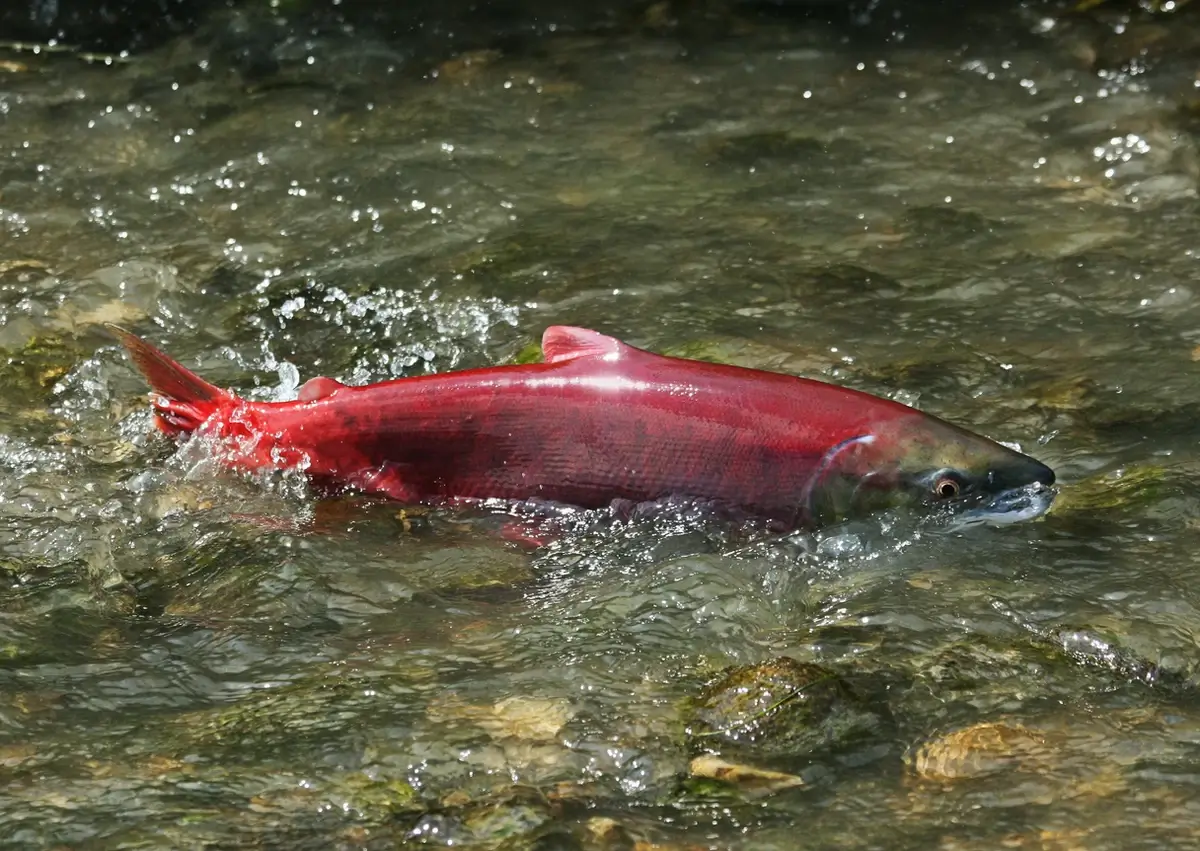

Image: seattleschild.com
9. Iconic Bridges Over Puget Sound
Puget Sound is spanned by several iconic bridges, showcasing engineering marvels.
The Tacoma Narrows Bridge, known for its original “Galloping Gertie” collapse in 1940, is a notable example.
These bridges are not just transportation links but also symbols of human ingenuity and resilience.
Their construction has had significant impacts on the region’s development and connectivity.
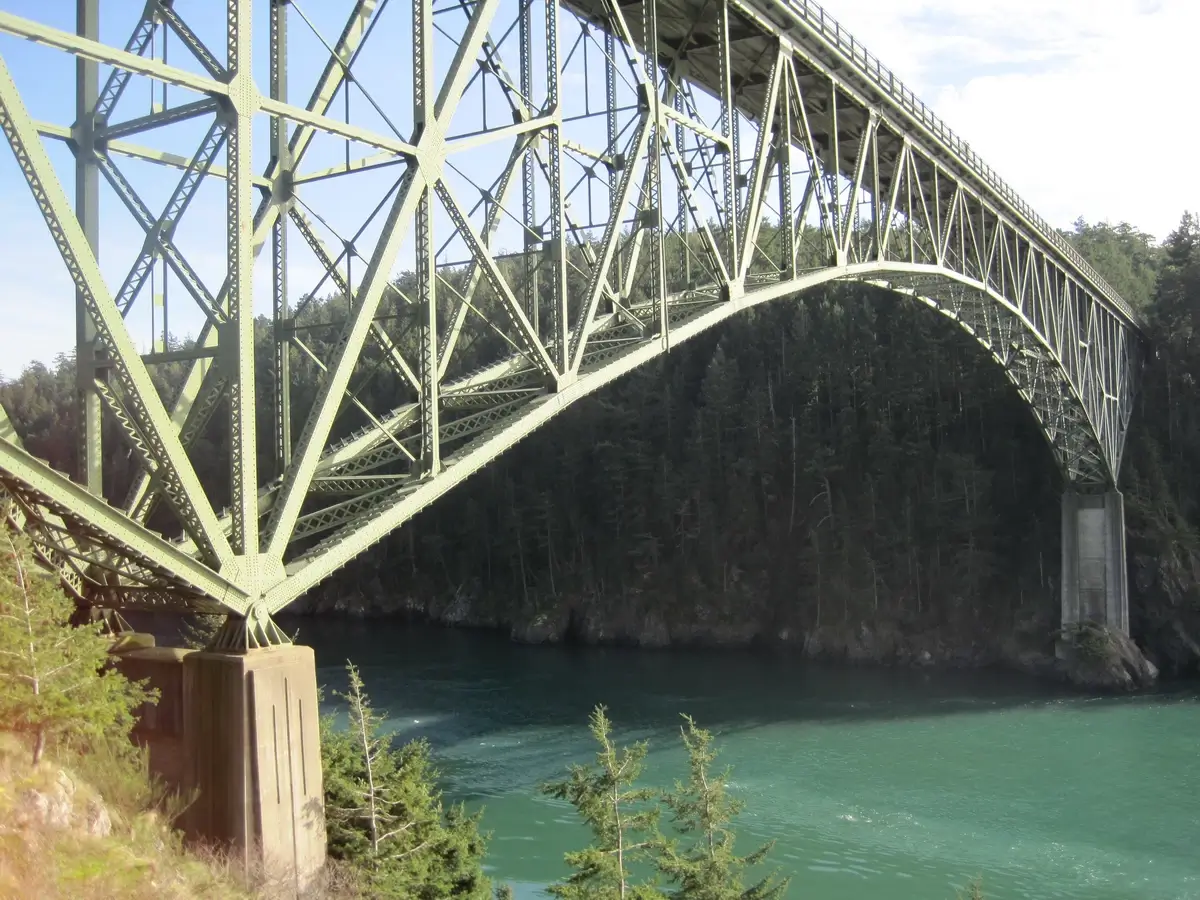

Chris Ballance / Flickr
10. Puget Sound’s Naval Heritage
Puget Sound has a rich naval heritage, marked by its long-standing association with the U.S. Navy.
The Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, established in 1891 in Bremerton, is a key facility for shipbuilding and maintenance.
The sound has been vital for naval operations, particularly during World War II.
Its strategic location and deep waters have made it an ideal site for naval activities and a significant contributor to local economies.
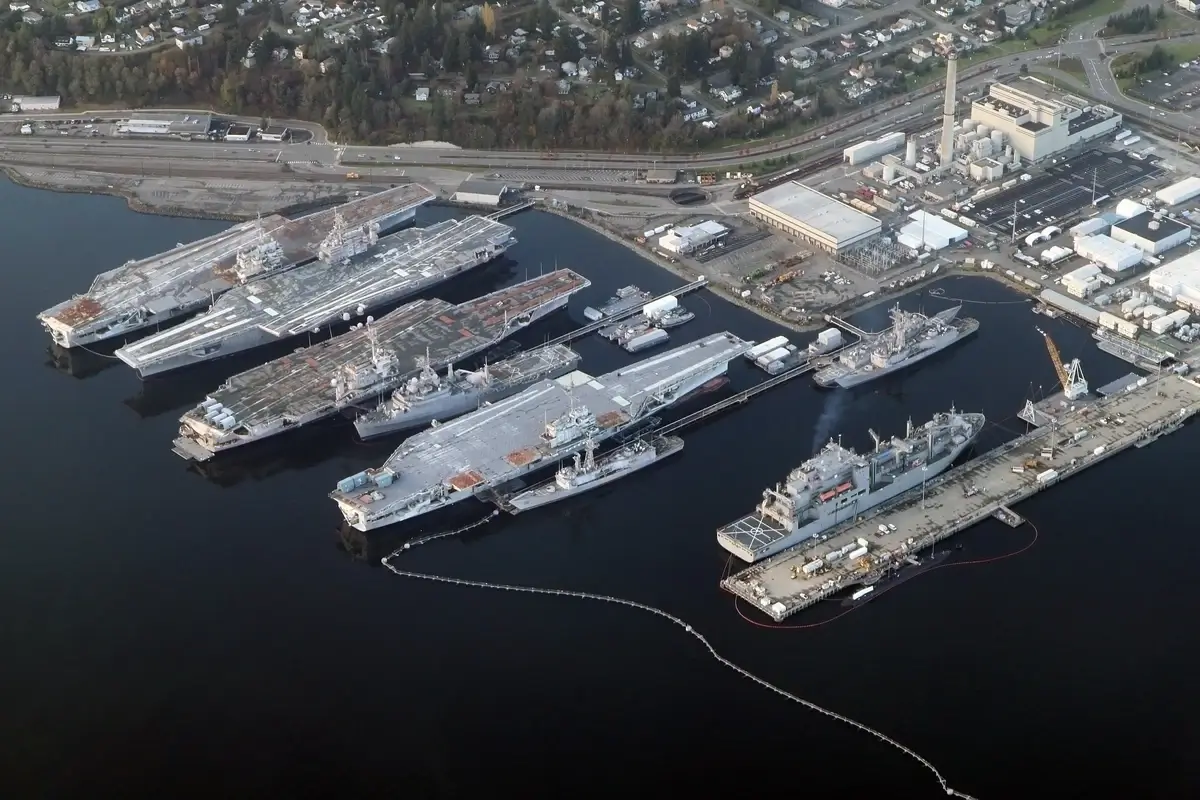

Image: Wikimedia Commons
11. The Tidal Phenomena of Puget Sound
Puget Sound experiences unique tidal phenomena due to its complex geography.
The sound’s tidal range can vary significantly, with some areas seeing changes of up to 14 feet.
These tides play a crucial role in the sound’s marine ecosystems, influencing nutrient distribution and habitat dynamics.
Understanding Puget Sound’s tides is essential for navigation, marine life, and coastal development.
12. Birdwatching Haven in Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a haven for birdwatchers, boasting a rich avian biodiversity.
Over 200 bird species, including migratory birds, waterfowl, and raptors, can be observed here.
The sound’s diverse habitats, from tidal flats to forested islands, provide ideal conditions for birdlife.
Birdwatching contributes to eco-tourism and helps in promoting conservation awareness.

Image: pugetsoundinstitute.org
13. Puget Sound’s Climate Influence
Puget Sound plays a significant role in the region’s climate.
Its waters moderate the local climate, leading to milder temperatures compared to inland areas.
The sound also influences precipitation patterns and cloud formations in the Pacific Northwest.
Understanding the climatic impact of Puget Sound is crucial for environmental planning and management.
14. Indigenous History of Puget Sound
Puget Sound holds profound significance in the indigenous history of the Pacific Northwest.
For thousands of years, native tribes have inhabited the shores of Puget Sound, relying on its resources for sustenance and cultural practices.
The Coast Salish people, in particular, have a deep connection with the sound, reflected in their traditions, art, and spirituality.
The sound’s name in the Lushootseed language, “Whulge,” reflects its importance in the indigenous cultural landscape.
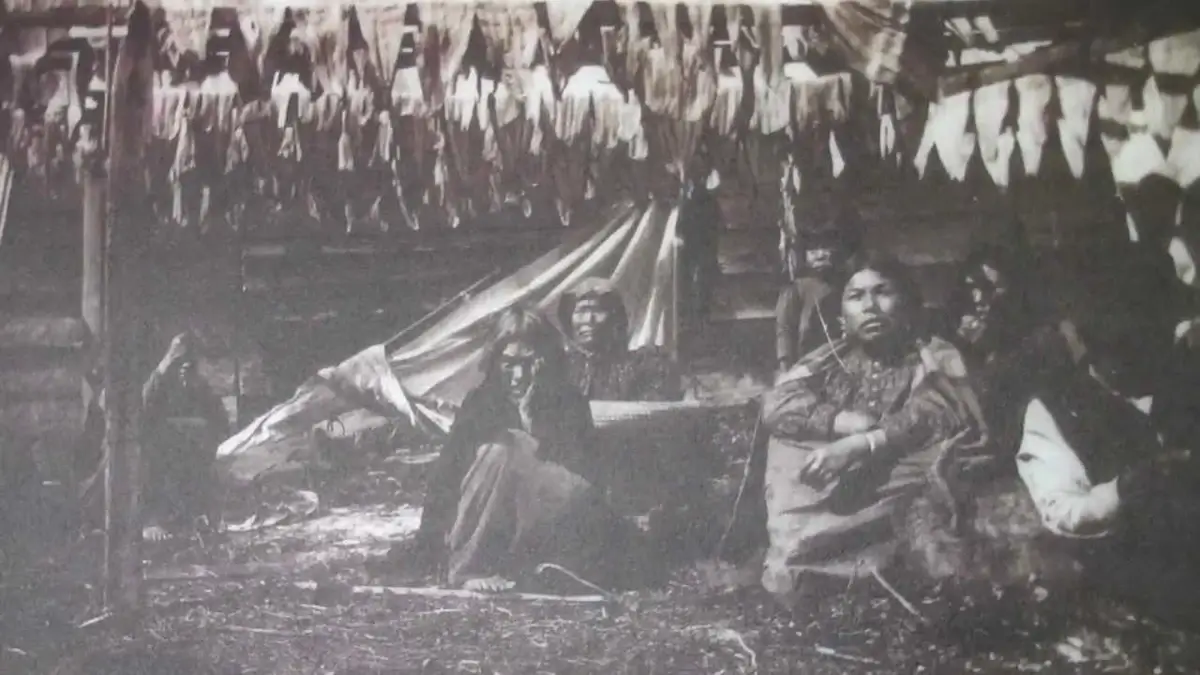

Image: brewminate.com
15. Conservation Efforts in Puget Sound
Conservation efforts in Puget Sound are critical for preserving its unique ecological and cultural heritage.
Various initiatives focus on habitat restoration, pollution reduction, and protecting endangered species.
Organizations like the Puget Sound Partnership work towards the sound’s ecological recovery and sustainable management.
Public awareness and community involvement are key to the success of these conservation efforts.
FAQ
What is Puget Sound known for?
Puget Sound is known for its breathtaking natural beauty, rich marine biodiversity, and significant cultural and historical importance. It’s a hub for maritime activities, including shipping, fishing, and recreational boating. The Sound is also famous for its unique ecosystem, hosting species like the Giant Pacific Octopus and resident orca populations. Additionally, its scenic landscapes and proximity to major cities like Seattle make it a popular destination for tourists and outdoor enthusiasts.
Why is it called a Puget Sound?
Puget Sound was named after Lieutenant Peter Puget, who served under British explorer George Vancouver. Vancouver explored the area in 1792 and named the sound in honor of Puget, who had conducted a detailed exploration of its southern reaches. This naming reflected the common practice of explorers naming new places after people involved in their discovery or significant figures from their homeland.
Why is Puget Sound so popular?
Puget Sound’s popularity stems from its stunning natural beauty, recreational opportunities, and rich biodiversity. It offers a wide range of activities such as boating, fishing, and whale watching, making it a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. The sound’s proximity to urban areas, combined with its natural and scenic beauty, also contributes to its allure as a getaway and a subject of artistic and cultural inspiration.
What is the Puget Sound myth?
The term “Puget Sound myth” typically refers to misconceptions or romanticized notions about the area. One common myth is the idea of Puget Sound being a pristine, untouched wilderness, which overlooks the extensive human influence and environmental challenges the region faces. Another myth relates to the historical perception of the Sound as an endless resource, ignoring the impacts of overfishing and pollution.
What are some historical facts about the Puget Sound?
Historically, Puget Sound has been a significant location for the indigenous Coast Salish people, who have inhabited its shores for thousands of years. In European history, it was first charted by George Vancouver in 1792. The sound played a crucial role in the maritime trade and later in naval activities, with the establishment of the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard in 1891. It was also a central point for the region’s logging and fishing industries.
What is at the bottom of Puget Sound?
At the bottom of Puget Sound, one finds a diverse landscape created by glacial activity, including deep basins, underwater hills, and valleys. The deepest point reaches about 930 feet near Point Jefferson. The sea floor hosts a variety of marine life and ecosystems, and it’s also the site of numerous shipwrecks, which add to the sound’s historical intrigue.
Who found Puget Sound?
Puget Sound was first charted by European explorers led by Captain George Vancouver in 1792. Lieutenant Peter Puget, a member of Vancouver’s expedition, is credited with conducting detailed exploration of the sound, leading to its naming after him. However, it’s important to acknowledge that indigenous peoples inhabited the region long before European exploration.
Why is Puget Sound so deep?
Puget Sound’s depth is largely attributed to its glacial history. During the last Ice Age, massive glaciers, particularly the Vashon Glacier, carved out the deep basins and channels of the sound. The retreating glaciers left behind these deep troughs and basins, creating the sound’s current topography, including its deepest points.